Clinical outcomes of tricuspid valve repair accompanying left-sided heart disease
- PMID: 29104738
- PMCID: PMC5661134
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i10.787
Clinical outcomes of tricuspid valve repair accompanying left-sided heart disease
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether the need for additional tricuspid valve repair is an independent risk factor when surgery is required for a left-sided heart disease.
Methods: One hundred and eighty patients (68 ± 12 years, 79 males) underwent tricuspid annuoplasty. Cox proportional-hazards regression model for multivariate analysis was performed for variables found significant in univariate analyses.
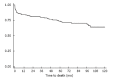
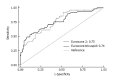
Results: Tricuspid regurgitation etiology was functional in 154 cases (86%), organic in 16 cases (9%), and mixed in 10 cases (6%), respectively. Postoperative mortality at 30 days was 11.7%. Mean follow-up was 51.7 mo with survival at 5 years of 73.5%. Risk factors for mortality were acute endocarditis [hazard ratio (HR) = 9.22 (95%CI: 2.87-29.62), P < 0.001], ischemic heart disease requiring myocardial revascularization [HR = 2.79 (1.26-6.20), P = 0.012], and aortic valve stenosis [HR = 2.6 (1.15-5.85), P = 0.021]. Significant predictive factors from univariate analyses were double-valve replacement combined with tricuspid annuloplasty [HR = 2.21 (1.11-4.39), P = 0.003] and preoperatively impaired ejection fraction [HR = 1.98 (1.04-3.92), P = 0.044]. However, successful mitral valve repair showed a protective effect [HR = 0.32 (0.10-0.98), P = 0.046]. Additionally, in instances where tricuspid regurgitation required the need for concomitant tricuspid valve repair, mortality predictor scores such as Euroscore 2 could be shortened to a simple Euroscore-tricuspid comprised of only 7 inputs. The explanation may lie in the fact that significant tricuspid regurgitation following left-sided heart disease represents an independent risk factor encompassing several other factors such as pulmonary arterial hypertension and dyspnea.
Conclusion: Tricuspid annuloplasty should be used more often as a concomitant procedure in the presence of relevant tricuspid regurgitation, although it usually reveals an overly delayed correction of a left-sided heart disease.
Keywords: Infective endocarditis; Mitral valve annuloplasty; Patient outcome assessment; Tricuspid regurgitation; Valvular annuloplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare having no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rogers JH, Bolling SF. Valve repair for functional tricuspid valve regurgitation: anatomical and surgical considerations. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;22:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Chikwe J, Anyanwu AC. Surgical strategies for functional tricuspid regurgitation. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;22:90–96. - PubMed
-
- Dreyfus GD, Corbi PJ, Chan KM, Bahrami T. Secondary tricuspid regurgitation or dilatation: which should be the criteria for surgical repair? Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79:127–132. - PubMed
-
- Vahanian A, Alfieri O, Andreotti F, Antunes MJ, Barón-Esquivias G, Baumgartner H, Borger MA, Carrel TP, De Bonis M, Evangelista A, Falk V, Lung B, Lancellotti P, Pierard L, Price S, Schäfers HJ, Schuler G, Stepinska J, Swedberg K, Takkenberg J, Von Oppell UO, Windecker S, Zamorano JL, Zembala M; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG); Joint Task Force on the Management of Valvular Heart Disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC); European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease (version 2012): the Joint Task Force on the Management of Valvular Heart Disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;42:S1–44. - PubMed
-
- Freed LA, Levy D, Levine RA, Larson MG, Evans JC, Fuller DL, Lehman B, Benjamin EJ. Prevalence and clinical outcome of mitral-valve prolapse. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources