External validation of four nephrometry scores for trans-peritoneal robotic partial nephrectomy
- PMID: 29104784
- PMCID: PMC5656368
- DOI: 10.5173/ceju.2017.1331
External validation of four nephrometry scores for trans-peritoneal robotic partial nephrectomy
Abstract
Introduction: External validation of four nephrometry scores (NS): Centrality index (C-index), arterial based complexity (ABC), preoperative aspects and dimensions used for an anatomical (PADUA) and radius expohytic/endophytic nearness anterior/posterior location (RENAL) scoring systems in patients who have undergone trans-peritoneal robotic assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN).
Material and methods: A prospective database for RAPN has been maintained. Individual NSs were performed on 3-dimensional reconstructions of MDCT/MRI studies retrospectively by a board certified uroradiologist. Univariate Cox Proportional-Hazard Regression Analysis was performed for each NSs to valuate its predictability for the following parameters: Warm Ischemia Time (WIT), Estimated Blood Loss (EBL), Operative Time (OT), Complication Rates and Positive Margin Rates.
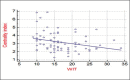
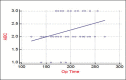
Results: 78 RAPNs were performed for suspected renal malignancies. The mean OT, EBL and WIT time was 186.5 minutes (SD - 33.8), 125.5 mls (SD - 188.91) and 16.7 minutes (SD - 5.6) respectively. The overall complication rate was 20.5% (16/78) of which only 2.6% (2/78) were Clavien Grade 3 or higher complications. The mean change in creatinine change at Day - 1 was 12.54 μmol/L (SD - 18.05). On the Cox regression analysis only the Centrality index predicted prolonged WIT with statistical significance: C-Index (0.02), ABC (0.2), PADUA (0.2), RENAL (0.9). ABC predicted operative time with statistical significance: C-index (0.45), ABC (0.0004), PADUA (0.25), RENAL (0.3). None of the NSs could predict overall complication: C-index (0.5), ABC (0.2), PADUA (0.13), RENAL (0.5). None of the NSs predicted EBL: C-index (0.3)0, ABC (0.8), PADUA (0.2), RENAL (0.7). None of the NSs predicted Positive Margin Rates: C-index (0.4), ABC (0.4), PADUA (0.9), RENAL (0.8).
Conclusions: C-index was able to predict prolonged WIT. ABC was a strong predictor of OT. PADUA and RENAL were poor predictors for all measured parameters.
Keywords: ABC; PADUA; centrality index; nephrometry scores; renal; robotic assisted partial nephrectomy.
Figures
References
-
- Ficarra V, Novara G, Secco S, et al. Preoperative aspects and dimensions used for an anatomical (PADUA) classification of renal tumours in patients who are candidates for nephron-sparing surgery. Eur Urol. 2009;56:786–793. - PubMed
-
- Kutikov A, Uzzo RG. The R.E.N.A.L. Nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized systemfor quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J Urol. 2009;182:844–853. - PubMed
-
- Simmons MN, Ching CB, Samplaski MK, Park CH, Gill IS. Kidney tumor location measurement using the C index method. J Urol. 2010;183:1708–1713. - PubMed
-
- Abroaf A, Vasdev N, Mohan SG, Adshead JM. Robotic partial nephrectomy: our first 30 consecutivecases. J Robot Surg. 2014;8:337–341.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous