SAM-VI RNAs selectively bind S-adenosylmethionine and exhibit similarities to SAM-III riboswitches
- PMID: 29106323
- PMCID: PMC5927728
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1399232
SAM-VI RNAs selectively bind S-adenosylmethionine and exhibit similarities to SAM-III riboswitches
Abstract
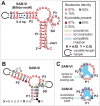
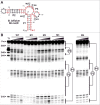
Five distinct riboswitch classes that regulate gene expression in response to the cofactor S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) or its metabolic breakdown product S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) have been reported previously. Collectively, these SAM- or SAH-sensing RNAs constitute the most abundant collection of riboswitches, and are found in nearly every major bacterial lineage. Here, we report a potential sixth member of this pervasive riboswitch family, called SAM-VI, which is predominantly found in Bifidobacterium species. SAM-VI aptamers selectively bind the cofactor SAM and strongly discriminate against SAH. The consensus sequence and structural model for SAM-VI share some features with the consensus model for the SAM-III riboswitch class, whose members are mainly found in lactic acid bacteria. However, there are sufficient differences between the two classes such that current bioinformatics methods separately cluster representatives of the two motifs. These findings highlight the abundance of RNA structures that can form to selectively recognize SAM, and showcase the ability of RNA to utilize diverse strategies to perform similar biological functions.
Keywords: SAM; aptamer; cofactor; gene regulation; metA; metK; noncoding RNA.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
