Pharmacological Efficacy/Toxicity of Drugs: A Comprehensive Update About the Dynamic Interplay of Microbes
- PMID: 29107046
- PMCID: PMC6712421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.10.031
Pharmacological Efficacy/Toxicity of Drugs: A Comprehensive Update About the Dynamic Interplay of Microbes
Abstract
Oral ingestion is a common, easy to access, route for therapeutic drugs to be delivered. The conception of the gastrointestinal tract as a passive physiological compartment has evolved toward a dynamic perspective of the same. Thus, microbiota plays an important role in contributing with additional metabolic capacities to its host as well as to its phenotypic heterogeneity. These adaptations in turn influence the efficacy and toxicity of a broad range of drugs. Notwithstanding, xenobiotics and therapeutic drugs affecting the microbiome's activity also significantly impact metabolism affecting different organs and tissues, and thereby drugs' toxicity/efficacy effects. Other physiological interfaces (i.e., gut, lungs, and skin) also represent complex media with features about microbiota's composition. In addition, there have been described key regulatory effects of microbes on immunotherapy, because of its potential harnessing the host immune system, mental disorders by modulating neuroendocrine systems and cancer. These alterations are responsible of physiological variations in the response(s) between individuals and populations. However, the study of population-based differences in intestinal microbial-related drug metabolism has been largely inferential. This review outlines major reciprocal implications between drugs and microbes regulatory capacities in pharmacotherapy.
Keywords: Efficacy; Metabolism; Microbes; Therapeutics; Toxicity.
Copyright © 2018 American Pharmacists Association®. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

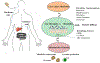
Similar articles
-
The effect of gut microbiota on drug metabolism.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013 Oct;9(10):1295-308. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2013.807798. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24033282 Review.
-
The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;12(1):31-40. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2016.1121234. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26569070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Metabolism by the Host and Gut Microbiota: A Partnership or Rivalry?Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Oct;43(10):1499-504. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.065714. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015. PMID: 26261284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The metabolic effect of gut microbiota on drugs.Drug Metab Rev. 2020 Feb;52(1):139-156. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2020.1718691. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Drug Metab Rev. 2020. PMID: 32116054 Review.
-
Cometabolism of microbes and host: implications for drug metabolism and drug-induced toxicity.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Nov;94(5):574-81. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2013.157. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23933971 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling the antimicrobial action of antidepressants on gut commensal microbes.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 21;10(1):17878. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74934-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33087796 Free PMC article.
-
More than Our Enemy: Making Space for the Microbiome in Pharmacy Education.Innov Pharm. 2022 Apr 2;13(1):10.24926/iip.v13i1.4553. doi: 10.24926/iip.v13i1.4553. eCollection 2022. Innov Pharm. 2022. PMID: 36304675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jia W, Li H, Zhao L, Nicholson JK. Gut microbiota: a potential new territory for drug targeting. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008; 7(2): 123–9. - PubMed
-
- Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006; 444: 1027–1031. - PubMed
-
- Blaut M Ecology and Physiology of the Intestinal Tract. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013; 358: 247–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

