African trypanosomiasis: Synthesis & SAR enabling novel drug discovery of ubiquinol mimics for trypanosome alternative oxidase
- PMID: 29107420
- PMCID: PMC5697954
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.067
African trypanosomiasis: Synthesis & SAR enabling novel drug discovery of ubiquinol mimics for trypanosome alternative oxidase
Abstract
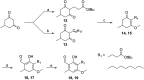
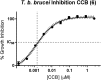
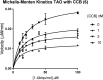
African trypanosomiasis is a parasitic disease affecting 5000 humans and millions of livestock animals in sub-Saharan Africa every year. Current treatments are limited, difficult to administer and often toxic causing long term injury or death in many patients. Trypanosome alternative oxidase is a parasite specific enzyme whose inhibition by the natural product ascofuranone (AF) has been shown to be curative in murine models. Until now synthetic methods to AF analogues have been limited, this has restricted both understanding of the key structural features required for binding and also how this chemotype could be developed to an effective therapeutic agent. The development of 3 amenable novel synthetic routes to ascofuranone-like compounds is described. The SAR generated around the AF chemotype is reported with correlation to the inhibition of T. b. brucei growth and corresponding selectivity in cytotoxic assessment in mammalian HepG2 cell lines. These methods allow access to greater synthetic diversification and have enabled the synthesis of compounds that have and will continue to facilitate further optimisation of the AF chemotype into a drug-like lead.
Keywords: Antiprotozoal agents; Medicinal chemistry; Oxidoreductase; Synthesis design.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Figures









References
-
- Brun R., Blum J., Chappuis F., Burri C. Human African trypanosomiasis. Lancet. 2010;375:148–159. - PubMed
-
- WHO Trypanosomiasis Human African (factsheet) 2017. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs259/en/
-
- Thomson R., Genovese G., Canon C., Kovacsics D., Higgins M.K., Carrington M., Winkler C.A., Kopp J., Rotimi C., Adeyemo A., Doumatey A., Ayodo G., Alper S.L., Pollak M.R., Friedman D.J., Raper J. Evolution of the primate trypanolytic factor APOL1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014;111:E2130–E2139. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morrison L.J., Marcello L., McCulloch R. Antigenic variation in the African trypanosome: molecular mechanisms and phenotypic complexity. Cell. Microbiol. 2009;11:1724–1734. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

