The utility of twins in developmental cognitive neuroscience research: How twins strengthen the ABCD research design
- PMID: 29107609
- PMCID: PMC5847422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2017.09.001
The utility of twins in developmental cognitive neuroscience research: How twins strengthen the ABCD research design
Abstract
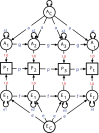
The ABCD twin study will elucidate the genetic and environmental contributions to a wide range of mental and physical health outcomes in children, including substance use, brain and behavioral development, and their interrelationship. Comparisons within and between monozygotic and dizygotic twin pairs, further powered by multiple assessments, provide information about genetic and environmental contributions to developmental associations, and enable stronger tests of causal hypotheses, than do comparisons involving unrelated children. Thus a sub-study of 800 pairs of same-sex twins was embedded within the overall Adolescent Brain and Cognitive Development (ABCD) design. The ABCD Twin Hub comprises four leading centers for twin research in Minnesota, Colorado, Virginia, and Missouri. Each site is enrolling 200 twin pairs, as well as singletons. The twins are recruited from registries of all twin births in each State during 2006-2008. Singletons at each site are recruited following the same school-based procedures as the rest of the ABCD study. This paper describes the background and rationale for the ABCD twin study, the ascertainment of twin pairs and implementation strategy at each site, and the details of the proposed analytic strategies to quantify genetic and environmental influences and test hypotheses critical to the aims of the ABCD study.
Keywords: Brain function; Brain structure; Environment; Heritability; Substance use; Twins.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Agrawal A., Nelson E.C., Littlefield A.K., Bucholz K.K., Degenhardt L., Henders A.K., Madden P.A.F., Martin N.G., Montgomery G.W., Pergadia M.L., Sher K.J., Heath A.C., Lynskey M.T. Cannabinoid receptor genotype moderation of the effects of childhood physical abuse on anhedonia and depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2012;69:732–740. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson L.S., Beverly W.T., Corey L.A., Murrelle L. The mid-Atlantic twin registry. Twin Res. 2002;5:449–455. - PubMed
-
- Bailey J.A., Samek D.R., Keyes M.A., Hill K.G., Hicks B.M., McGue M., Iacono W.G., Epstein M., Catalano R.F., Haggerty K.P., Hawkins J.D. General and substance-specific predictors of young adult nicotine dependence, alcohol use disorder, and problem behavior: replication in two samples. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;138:161–168. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U24 DA041147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA051018/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041093/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041123/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA051038/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041022/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041089/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041106/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041048/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041148/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041174/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD027802/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

