Lopinavir plus nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors, lopinavir plus raltegravir, or lopinavir monotherapy for second-line treatment of HIV (EARNEST): 144-week follow-up results from a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 29108797
- PMCID: PMC5739875
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30630-8
Lopinavir plus nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors, lopinavir plus raltegravir, or lopinavir monotherapy for second-line treatment of HIV (EARNEST): 144-week follow-up results from a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Millions of HIV-infected people worldwide receive antiretroviral therapy (ART) in programmes using WHO-recommended standardised regimens. Recent WHO guidelines recommend a boosted protease inhibitor plus raltegravir as an alternative second-line combination. We assessed whether this treatment option offers any advantage over the standard protease inhibitor plus two nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) second-line combination after 144 weeks of follow-up in typical programme settings.
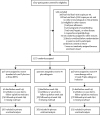
Methods: We analysed the 144-week outcomes at the completion of the EARNEST trial, a randomised controlled trial done in HIV-infected adults or adolescents in 14 sites in five sub-Saharan African countries (Uganda, Zimbabwe, Malawi, Kenya, Zambia). Participants were those who were no longer responding to non-NRTI-based first-line ART, as assessed with WHO criteria, confirmed by viral-load testing. Participants were randomly assigned to receive a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor (lopinavir 400 mg with ritonavir 100 mg, twice per day) plus two or three clinician-selected NRTIs (protease inhibitor plus NRTI group), protease inhibitor plus raltegravir (400 mg twice per day; protease inhibitor plus raltegravir group), or protease inhibitor monotherapy (plus raltegravir induction for first 12 weeks, re-intensified to combination therapy after week 96; protease inhibitor monotherapy group). Randomisation was by computer-generated randomisation sequence, with variable block size. The primary outcome was viral load of less than 400 copies per mL at week 144, for which we assessed non-inferiority with a one-sided α of 0·025, and superiority with a two-sided α of 0·025. The EARNEST trial is registered with ISRCTN, number 37737787.
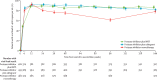
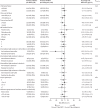
Findings: Between April 12, 2010, and April 29, 2011, 1837 patients were screened for eligibility, of whom 1277 patients were randomly assigned to an intervention group. In the primary (complete-case) analysis at 144 weeks, 317 (86%) of 367 in the protease inhibitor plus NRTI group had viral loads of less than 400 copies per mL compared with 312 (81%) of 383 in the protease inhibitor plus raltegravir group (p=0·07; lower 95% confidence limit for difference 10·2% vs specified non-inferiority margin 10%). In the protease inhibitor monotherapy group, 292 (78%) of 375 had viral loads of less than 400 copies per mL; p=0·003 versus the protease inhibitor plus NRTI group at 144 weeks. There was no difference between groups in serious adverse events, grade 3 or 4 adverse events (total or ART-related), or events that resulted in treatment modification.
Interpretation: Protease inhibitor plus raltegravir offered no advantage over protease inhibitor plus NRTI in virological efficacy or safety. In the primary analysis, protease inhibitor plus raltegravir did not meet non-inferiority criteria. A regimen of protease inhibitor with NRTIs remains the best standardised second-line regimen for use in programmes in resource-limited settings.
Funding: European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP), UK Medical Research Council, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Irish Aid, Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, Instituto Superiore di Sanita, Merck, ViiV Healthcare, WHO.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
The unexpected success of NRTIs in second-line treatment.Lancet Infect Dis. 2018 Jan;18(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30631-X. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29108798 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gilks CF, Crowley S, Ekpini R. The WHO public-health approach to antiretroviral treatment against HIV in resource-limited settings. Lancet. 2006;368:505–510. - PubMed
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2016. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: recommendations for a public health approach. - PubMed
-
- Paton NI, Kityo C, Hoppe A. Assessment of second-line antiretroviral regimens for HIV therapy in Africa. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:234–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

