Charged residues in the H-NS linker drive DNA binding and gene silencing in single cells
- PMID: 29109287
- PMCID: PMC5703333
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1716721114
Charged residues in the H-NS linker drive DNA binding and gene silencing in single cells
Abstract
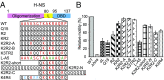
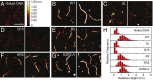
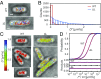
Nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs) facilitate chromosome organization in bacteria, but the precise mechanism remains elusive. H-NS is a NAP that also plays a major role in silencing pathogen genes. We used genetics, single-particle tracking in live cells, superresolution microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and molecular dynamics simulations to examine H-NS/DNA interactions in single cells. We discovered a role for the unstructured linker region connecting the N-terminal oligomerization and C-terminal DNA binding domains. In the present work we demonstrate that linker amino acids promote engagement with DNA. In the absence of linker contacts, H-NS binding is significantly reduced, although no change in chromosome compaction is observed. H-NS is not localized to two distinct foci; rather, it is scattered all around the nucleoid. The linker makes DNA contacts that are required for gene silencing, while chromosome compaction does not appear to be an important H-NS function.
Keywords: H-NS; atomic force microscopy; nucleoid-associated proteins; single-particle tracking; superresolution microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dimerization site 2 of the bacterial DNA-binding protein H-NS is required for gene silencing and stiffened nucleoprotein filament formation.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 15;293(24):9496-9505. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001425. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29695505 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome organization by a nucleoid-associated protein in live bacteria.Science. 2011 Sep 9;333(6048):1445-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1204697. Science. 2011. PMID: 21903814 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Assembly of the Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Type 4 Pilus.Structure. 2019 Jul 2;27(7):1082-1093.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.03.021. Epub 2019 May 2. Structure. 2019. PMID: 31056419 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of bacterial H-NS protein.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Dec 15;44(6):1561-1569. doi: 10.1042/BST20160190. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27913665 Review.
-
The Impact of Gene Silencing on Horizontal Gene Transfer and Bacterial Evolution.Adv Microb Physiol. 2016;69:157-186. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Adv Microb Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27720010 Review.
Cited by
-
Global H-NS counter-silencing by LuxR activates quorum sensing gene expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 10;48(1):171-183. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1089. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31745565 Free PMC article.
-
A single molecule analysis of H-NS uncouples DNA binding affinity from DNA specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 2;46(19):10216-10224. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky826. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30239908 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic context effects can override canonical cis regulatory elements in Escherichia coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 14;50(18):10360-10375. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac787. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36134716 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary and functional divergence of Sfx, a plasmid-encoded H-NS homolog, underlies the regulation of IncX plasmid conjugation.mBio. 2025 Feb 5;16(2):e0208924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02089-24. Epub 2024 Dec 23. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39714162 Free PMC article.
-
Redefining the H-NS protein family: a diversity of specialized core and accessory forms exhibit hierarchical transcriptional network integration.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Oct 9;48(18):10184-10198. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa709. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32894292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prajapat MK, Saini S. Interplay between Fur and HNS in controlling virulence gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium. Comput Biol Med. 2012;42:1133–1140. - PubMed
-
- Navarre WW, et al. Selective silencing of foreign DNA with low GC content by the H-NS protein in Salmonella. Science. 2006;313:236–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

