Host-based lipid inflammation drives pathogenesis in Francisella infection
- PMID: 29109289
- PMCID: PMC5703311
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1712887114
Host-based lipid inflammation drives pathogenesis in Francisella infection
Abstract
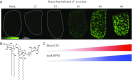
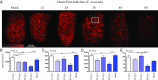
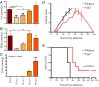
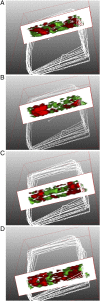
Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) was used to elucidate host lipids involved in the inflammatory signaling pathway generated at the host-pathogen interface during a septic bacterial infection. Using Francisella novicida as a model organism, a bacterial lipid virulence factor (endotoxin) was imaged and identified along with host phospholipids involved in the splenic response in murine tissues. Here, we demonstrate detection and distribution of endotoxin in a lethal murine F. novicida infection model, in addition to determining the temporally and spatially resolved innate lipid inflammatory response in both 2D and 3D renderings using MSI. Further, we show that the cyclooxygenase-2-dependent lipid inflammatory pathway is responsible for lethality in F. novicida infection due to overproduction of proinflammatory effectors including prostaglandin E2. The results of this study emphasize that spatial determination of the host lipid components of the immune response is crucial to identifying novel strategies to effectively address highly pathogenic and lethal infections stemming from bacterial, fungal, and viral origins.
Keywords: cyclooxygenase pathway; host–pathogen interaction; lipid inflammation; mass spectrometry imaging; microbial pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Raetz CRH. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: Mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Rietschel ET. Innate immune sensing and its roots: The story of endotoxin. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Trent MS, Stead CM, Tran AX, Hankins JV. Diversity of endotoxin and its impact on pathogenesis. J Endotoxin Res. 2006;12:205–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

