Inhibition of Pro-inflammatory and Anti-apoptotic Biomarkers during Experimental Oral Cancer Chemoprevention by Dietary Black Raspberries
- PMID: 29109723
- PMCID: PMC5660285
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01325
Inhibition of Pro-inflammatory and Anti-apoptotic Biomarkers during Experimental Oral Cancer Chemoprevention by Dietary Black Raspberries
Abstract
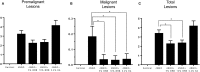
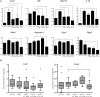
Oral cancer continues to be a significant public health problem worldwide. Recently conducted clinical trials demonstrate the ability of black raspberries (BRBs) to modulate biomarkers of molecular efficacy that supports a chemopreventive strategy against oral cancer. However, it is essential that a preclinical animal model of black raspberry (BRB) chemoprevention which recapitulates human oral carcinogenesis be developed, so that we can validate biomarkers and evaluate potential mechanisms of action. We therefore established the ability of BRBs to inhibit oral lesion formation in a carcinogen-induced rat oral cancer model and examined potential mechanisms. F344 rats were administered 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4NQO) (20 µg/ml) in drinking water for 14 weeks followed by regular drinking water for 6 weeks. At week 14, rats were fed a diet containing either 5 or 10% BRB, or 0.4% ellagic acid (EA), a BRB phytochemical. Dietary administration of 5 and 10% BRB reduced oral lesion incidence and multiplicity by 39.3 and 28.6%, respectively. Histopathological analyses demonstrate the ability of BRBs and, to a lesser extent EA, to inhibit the progression of oral cancer. Oral lesion inhibition by BRBs was associated with a reduction in the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory biomarkers Cxcl1, Mif, and Nfe2l2 as well as the anti-apoptotic and cell cycle associated markers Birc5, Aurka, Ccna1, and Ccna2. Cellular proliferation (Ki-67 staining) in tongue lesions was inhibited by BRBs and EA. Our study demonstrates that, in the rat 4NQO oral cancer model, dietary administration of BRBs inhibits oral carcinogenesis via inhibition of pro-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic pathways.
Keywords: biomarker; black raspberry; chemoprevention; oral cancer; pro-inflammatory.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metabolic Regulation of Glycolysis and AMP Activated Protein Kinase Pathways during Black Raspberry-Mediated Oral Cancer Chemoprevention.Metabolites. 2019 Jul 11;9(7):140. doi: 10.3390/metabo9070140. Metabolites. 2019. PMID: 31336728 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoprevention of oral cancer by topical application of black raspberries on high at-risk mucosa.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014 Dec;118(6):674-83. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25457886 Free PMC article.
-
Black raspberry extract inhibits regulatory T-cell activity in a murine model of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma chemoprevention.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 9;13:932742. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.932742. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36016924 Free PMC article.
-
Berries vs. Disease: Revenge of the Phytochemicals.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 9;17(1):84. doi: 10.3390/ph17010084. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk biomarkers and current strategies for cancer chemoprevention.J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1996;25:1-14. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1996. PMID: 9027592 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary Flavonoids for Immunoregulation and Cancer: Food Design for Targeting Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Jun 29;8(7):202. doi: 10.3390/antiox8070202. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31261915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of PI3K Isoform p110γ Increases Both Anti-Tumor and Immunosuppressive Responses to Aggressive Murine Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Low Immunogenicity.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 25;13(5):953. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050953. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668795 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Phytochemicals in Oral Cancer Prevention and Therapy: A Review of the Evidence.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 6;10(8):1150. doi: 10.3390/biom10081150. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32781654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT1 inhibits T-cell exhaustion and myeloid derived suppressor cell accumulation to promote antitumor immune responses in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2020 Mar 15;146(6):1717-1729. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32781. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31709529 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the oral glucocorticoid system during black raspberry mediated oral cancer chemoprevention.Carcinogenesis. 2022 Feb 11;43(1):28-39. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgab118. Carcinogenesis. 2022. PMID: 34888650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McCormick DL, Phillips JM, Horn TL, Johnson WD, Steele VE, Lubet RA. Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in rat oral cancers and prevention of oral carcinogenesis in rats by selective and nonselective COX inhibitors. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) (2010) 3:73–81.10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0151 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

