Rapid Construction of Complex Plant RNA Virus Infectious cDNA Clones for Agroinfection Using a Yeast-E. coli-Agrobacterium Shuttle Vector
- PMID: 29112135
- PMCID: PMC5707539
- DOI: 10.3390/v9110332
Rapid Construction of Complex Plant RNA Virus Infectious cDNA Clones for Agroinfection Using a Yeast-E. coli-Agrobacterium Shuttle Vector
Abstract
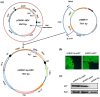
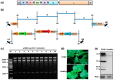
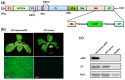
The availability of infectious full-length clone is indispensable for reverse genetics studies of virus biology, pathology and construction of viral vectors. However, for RNA viruses with large genome sizes or those exhibiting inherent cloning difficulties, procedure to generate biologically active circular DNA (cDNA) clones can be time-consuming or technically challenging. Here we have constructed a yeast-Escherichia coli-Agrobacterium shuttle vector that enables highly efficient homologous recombination in yeast for assembly of Agrobacterium compatible plant virus clones. Using this vector, we show that infectious cDNA clones of a plant negative-stranded RNA virus, sonchus yellow net rhabdovirus, can be rapidly assembled. In addition, one-step assembly of infectious clones of potato virus Y in yeast, either with or without intron, was readily achieved from as many as eight overlapping DNA fragments. More importantly, the recovered yeast plasmids can be transformed directly into Agrobacterium for inoculation, thereby obviating the E. coli cloning steps and associated toxicity issues. This method is rapid, highly efficient and cost-effective and should be readily applicable to a broad range of plant viruses.
Keywords: agroinfection; infectious cDNA clone; potato virus Y; potyvirus; rhabdovirus; sonchus yellow net virus; yeast homologous recombination; yeast-E.coli-Agrobacterium shuttle vector.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Generation of a Triple-Shuttling Vector and the Application in Plant Plus-Strand RNA Virus Infectious cDNA Clone Construction.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 13;24(6):5477. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065477. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982550 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Construction of Stable Infectious Full-Length cDNA Clone of Papaya Leaf Distortion Mosaic Virus Using In-Fusion Cloning.Viruses. 2015 Dec 1;7(12):6241-50. doi: 10.3390/v7122935. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26633465 Free PMC article.
-
Site-directed mutagenesis and generation of chimeric viruses by homologous recombination in yeast to facilitate analysis of plant-virus interactions.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004 Jun;17(6):571-6. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.6.571. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004. PMID: 15195939
-
Infectious full-length clones of plant viruses and their use for construction of viral vectors.Acta Virol. 2007;51(4):223-37. Acta Virol. 2007. PMID: 18197730 Review.
-
Development of Model Systems for Plant Rhabdovirus Research.Adv Virus Res. 2018;102:23-57. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2018.06.008. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Adv Virus Res. 2018. PMID: 30266175 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Rice Stripe Tenuivirus Minireplicon Reverse Genetics Systems Suitable for Analyses of Viral Replication and Intercellular Movement.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 23;12:655256. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.655256. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33833749 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for the Construction of Cassava Brown Streak Disease Viral Infectious Clones.Mol Biotechnol. 2019 Feb;61(2):93-101. doi: 10.1007/s12033-018-0139-7. Mol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30484144 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility factor StEXA1 interacts with StnCBP to facilitate potato virus Y accumulation through the stress granule-dependent RNA regulatory pathway in potato.Hortic Res. 2022 Feb 13;9:uhac159. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac159. eCollection 2022. Hortic Res. 2022. PMID: 36204208 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and biological characterization of infectious full-length cDNA clones of two viruses in Paris yunnanensis, including a novel potyvirus.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):473. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84226-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747256 Free PMC article.
-
Home-made enzymatic premix and Illumina sequencing allow for one-step Gibson assembly and verification of virus infectious clones.Phytopathol Res. 2020;2:36. doi: 10.1186/s42483-020-00077-4. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Phytopathol Res. 2020. PMID: 33768973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leiser R.M., Ziegler-Graff V., Reutenauer A., Herrbach E., Lemaire O., Guilley H., Richards K., Jonard G. Agroinfection as an alternative to insects for infecting plants with beet western yellows luteovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1992;89:9136–9140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

