PSN-PC: A Novel Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Peptide from the Skin Secretion of Phyllomedusa-camba with Cytotoxicity on Human Lung Cancer Cell
- PMID: 29112170
- PMCID: PMC6150266
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22111896
PSN-PC: A Novel Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Peptide from the Skin Secretion of Phyllomedusa-camba with Cytotoxicity on Human Lung Cancer Cell
Abstract
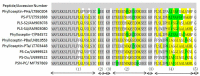
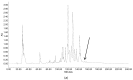
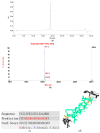
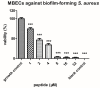
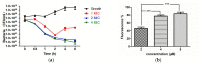
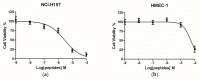
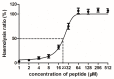
Peptides derived from amphibian skin secretion are promising drug prototypes for combating widespread infection. In this study, a novel peptide belonging to the phylloseptin family of antimicrobial peptides was isolated from the skin secretion of the Phyllomedusa camba, namely phylloseptin-PC (PSN-PC). The biosynthetic precursor was obtained by molecular cloning and the mature peptide sequence was confirmed through tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) fragmentation sequencing in the skin secretion. The synthetic replicate exhibited a broad spectrum antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus,Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans at concentrations of 2, 2, 8, 32 and 2 µM, respectively. It also showed the capability of eliminating S. aureus biofilm with a minimal biofilm eradication concentration of 8 µM. The haemolysis of this peptide was not significant at low concentrations but had a considerable increase at high concentrations. Additionally, this peptide showed an anti-proliferation effect on the non-small cell lung cancer cell line (NCI-H157), with low cytotoxicity on the human microvascular endothelial cell line (HMEC-1). The discovery of the novel peptide may provide useful clues for new drug discoveries.
Keywords: anti-biofilm activity; antimicrobial peptide; cancer cell cytotoxicity; phylloseptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phylloseptin-PBa--A Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide from the Skin Secretion of the Peruvian Purple-Sided Leaf Frog (Phyllomedusa Baltea) Which Exhibits Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Dec 1;7(12):5182-93. doi: 10.3390/toxins7124878. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26633506 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Phylloseptins that Defense against Gram-Positive Bacteria and Inhibit the Proliferation of the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line, from the Skin Secretions of Phyllomedusa Frogs.Molecules. 2017 Aug 29;22(9):1428. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091428. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28850103 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Novel Bacterial Cell-Penetrating Phylloseptins in Defensive Skin Secretions of the South American Hylid Frogs, Phyllomedusa duellmani and Phyllomedusa coelestis.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Aug 31;8(9):255. doi: 10.3390/toxins8090255. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27589802 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances in the study of synergistic effect of anti-biofilm agents].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Mar;47(3):339-45. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22645757 Review. Chinese.
-
Anti-biofilm peptides as a new weapon in antimicrobial warfare.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Oct;33:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.05.016. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27318321 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Road from Host-Defense Peptides to a New Generation of Antimicrobial Drugs.Molecules. 2018 Feb 1;23(2):311. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020311. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29389911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Applications and Anticancer Effects of Antimicrobial Peptides: From Bench to Bedside.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 23;12:819563. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.819563. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35280755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modification Strategy of D-leucine Residue Addition on a Novel Peptide from Odorrana schmackeri, with Enhanced Bioactivity and In Vivo Efficacy.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;13(9):611. doi: 10.3390/toxins13090611. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34564615 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effect of Thymol-Ciprofloxacin Combination on Planktonic Cells and Biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Curr Microbiol. 2023 Nov 29;81(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03546-z. Curr Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38019310
-
The Addition of a Synthetic LPS-Targeting Domain Improves Serum Stability While Maintaining Antimicrobial, Antibiofilm, and Cell Stimulating Properties of an Antimicrobial Peptide.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 8;10(7):1014. doi: 10.3390/biom10071014. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32650576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kückelhaus S.A., Leite J.R.S., Muniz-Junqueira M.I., Sampaio R.N., Bloch C., Tosta C.E. Antiplasmodial and antileishmanial activities of phylloseptin-1, an antimicrobial peptide from the skin secretion of Phyllomedusa azurea (Amphibia) Exp. Parasitol. 2009;123:11–16. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2009.05.002. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

