Interleukin 1β inhibition contributes to the antinociceptive effects of voluntary exercise on ischemia/reperfusion-induced hypersensitivity
- PMID: 29112534
- PMCID: PMC5927851
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001094
Interleukin 1β inhibition contributes to the antinociceptive effects of voluntary exercise on ischemia/reperfusion-induced hypersensitivity
Abstract
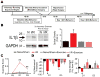
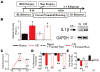
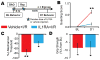
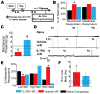
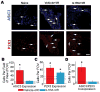
Issues of peripheral circulation have been increasingly suggested as an underlying cause of musculoskeletal pain in many conditions, including sickle cell anemia and peripheral vascular disease. We have previously shown in our model of transient ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury of the forelimb that individual group III and IV muscle afferents display altered chemosensitivity and mechanical thresholds 1 day after injury. Functional alterations corresponded to increased evoked and spontaneous pain-related behaviors and decreased muscle strength and voluntary activity-all actions that echo clinical symptoms of ischemic myalgia. These behavioral and physiological changes appeared to originate in part from the action of increased interleukin 1β (IL1β) in the injured muscles at its upregulated IL1 receptor 1 within the dorsal root ganglion. Here, we describe that two days of voluntary wheel running prior to I/R blocks both injury-induced IL1β enhancement and the subsequent development of ischemic myalgia-like behaviors. Furthermore, the protective effects of 2 days prior exercise on the I/R-evoked increases in pain-related behaviors were also paralleled with systemic injection of the IL1 receptor antagonist during I/R. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist treatment additionally prevented the I/R-induced changes in mechanical and chemical sensitivity of individual primary muscle afferents. Altogether, these data strengthen the evidence that transient I/R injury sensitizes group III and IV muscle afferents via increased IL1β in the muscles to stimulate ischemic myalgia development. Targeting IL1β may, therefore, be an effective treatment strategy for this insidious type of muscle pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

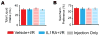
Similar articles
-
Muscle IL1β Drives Ischemic Myalgia via ASIC3-Mediated Sensory Neuron Sensitization.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 29;36(26):6857-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4582-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27358445 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitization of group III and IV muscle afferents in the mouse after ischemia and reperfusion injury.J Pain. 2014 Dec;15(12):1257-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2014.09.003. J Pain. 2014. PMID: 25245401 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Modulation of Nociception and Cardiovascular Reflexes during Peripheral Ischemia through P2Y1 Receptor-Dependent Sensitization of Muscle Afferents.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 6;36(1):19-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2856-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26740646 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in primary muscle afferent sensitization following ischemia and reperfusion injury.Biol Sex Differ. 2018 Jan 3;9(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13293-017-0163-5. Biol Sex Differ. 2018. PMID: 29298725 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Mechanisms of Ischemic Myalgia.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Dec 22;11:419. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00419. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29311839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of routine exercise on the peripheral immune system to prevent and alleviate pain.Neurobiol Pain. 2023 Mar 21;13:100126. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2023.100126. eCollection 2023 Jan-Jul. Neurobiol Pain. 2023. PMID: 37179769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences and mechanisms of muscle pain.Curr Opin Physiol. 2019 Oct;11:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cophys.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Curr Opin Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31245656 Free PMC article.
-
Normalization of Neuroinflammation: A New Strategy for Treatment of Persistent Pain and Memory/Emotional Deficits in Chronic Pain.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Sep 9;15:5201-5233. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S379093. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36110505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of Hyaluronic Acid in Skeletal Muscle Induces Decreased Voluntary Activity via Chemosensitive Muscle Afferent Sensitization in Male Mice.eNeuro. 2022 Apr 13;9(2):ENEURO.0522-21.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0522-21.2022. Print 2022 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 35387844 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions and Trends of Interleukins, PAI-1, CRP, and TNF-α in Inflammatory Responses during the Perioperative Period of Joint Arthroplasty: Implications for Pain Management-A Narrative Review.J Pers Med. 2024 May 17;14(5):537. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050537. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ali FN, Carman TL. Medical management for chronic atherosclerotic peripheral arterial disease. Drugs. 2012;72(16):2073–2085. - PubMed
-
- Baamonde A, Curto-Reyes V, Juarez L, Meana A, Hidalgo A, Menendez L. Antihyperalgesic effects induced by the IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra and increased IL-1beta levels in inflamed and osteosarcoma-bearing mice. Life Sci. 2007;81(8):673–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

