Combined targeting of Raf and Mek synergistically inhibits tumorigenesis in triple negative breast cancer model systems
- PMID: 29113345
- PMCID: PMC5655240
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20534
Combined targeting of Raf and Mek synergistically inhibits tumorigenesis in triple negative breast cancer model systems
Abstract
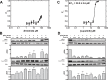
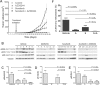
Aberrant Ras-MAPK signaling from receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2), is a hallmark of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC); thus providing rationale for targeting the Ras-MAPK pathway. Components of this EGFR/HER2-Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk pathway were co-targeted in the MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 human TNBC cell lines, and in vitro effects on signaling and cytotoxicity, as well as in vivo effects on xenograft tumor growth and metastasis were assessed. The dual EGFR/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib (LPN) displayed greater cytotoxic potency and MAPK signaling inhibition than the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib, suggesting both EGFR and HER2 contribute to MAPK signaling in this TNBC model. The Raf inhibitor sorafenib (SFN) or the Mek inhibitor U0126 suppressed MAPK signaling to a greater extent than LPN; which correlated with greater cytotoxic potency of SFN, but not U0126. However, U0126 potentiated the cytotoxic efficacy of LPN and SFN in an additive and synergistic manner, respectively. This in-series Raf-Mek co-targeting synergy was recapitulated in orthotopic mouse xenografts, where SFN and the Mek inhibitor selumitinib (AZD6244) inhibited primary tumor growth and pulmonary metastasis. Raf and Mek co-inhibition exhibits synergy in TNBC models and represent a promising combination therapy for this aggressive breast cancer type.
Keywords: Mek; Raf; selumitinib; synergy; triple negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Flavopiridol synergizes with sorafenib to induce cytotoxicity and potentiate antitumorigenic activity in EGFR/HER-2 and mutant RAS/RAF breast cancer model systems.Neoplasia. 2013 Aug;15(8):939-51. doi: 10.1593/neo.13804. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23908594 Free PMC article.
-
Amplified Ras-MAPK signal states correlate with accelerated EGFR internalization, cytostasis and delayed HER2 tumor onset in Fer-deficient model systems.Oncogene. 2015 Jul 30;34(31):4109-17. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.340. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25347743
-
Growth and molecular interactions of the anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab and the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin in gefitinib-resistant MDA-MB-468 cells: new prospects in the treatment of triple-negative/basal-like breast cancer.Int J Oncol. 2008 Dec;33(6):1165-76. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19020749
-
Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer.Oncogene. 2007 May 14;26(22):3291-310. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210422. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17496923 Review.
-
Cancer resistance to therapies against the EGFR-RAS-RAF pathway: The role of MEK.Cancer Treat Rev. 2017 Feb;53:61-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.12.001. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017. PMID: 28073102 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein phosphatase 2A activation as a therapeutic strategy for managing MYC-driven cancers.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 17;295(3):757-770. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011443. Epub 2019 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31822503 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Fish Oil and Selenium Enhances Anticancer Efficacy and Targets Multiple Signaling Pathways in Anti-VEGF Agent Treated-TNBC Tumor-Bearing Mice.Mar Drugs. 2021 Mar 29;19(4):193. doi: 10.3390/md19040193. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33805447 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Autophagy-Mediated Treatment Resistance in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 11;11(11):1775. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111775. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31717997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Molecular Classifications of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving Patient Selection for Treatment.Cancer Discov. 2019 Feb;9(2):176-198. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1177. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 30679171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of MEK Inhibitor and the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway Inhibition for the Therapy of Colon Cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019 Apr;25(2):769-775. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00592-6. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 30706361
References
-
- Klijn JG, Berns PM, Bontenbal M, Alexieva-Figusch J, Foekens JA. Clinical breast cancer, new developments in selection and endocrine treatment of patients. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;43:211–21. - PubMed
-
- Klijn JG, Berns PM, Schmitz PI, Foekens JA. The clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) in human breast cancer: a review on 5232 patients. Endocr Rev. 1992;13:3–17. - PubMed
-
- Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1995;19:183–232. - PubMed
-
- Tsutsui S, Kataoka A, Ohno S, Murakami S, Kinoshita J, Hachitanda Y. Prognostic and predictive value of epidermal growth factor receptor in recurrent breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:3454–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

