Oxidative stress-induced diseases and tea polyphenols
- PMID: 29113421
- PMCID: PMC5655316
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20887
Oxidative stress-induced diseases and tea polyphenols
Abstract
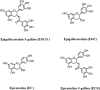
Reactive oxide species are the middle products of normal metabolism, and play a crucial role in cell signaling transduction. On the contrary, accumulation of excess reactive oxide species results in oxidative stress that often brings multifarious impairment to cells, including decrease of ATP level in cells, elevation of cytosolic Ca2+, DNA damage, dysfunction of biological function in lipid bilayer and so on. These effects will finally lead to all kinds of diseases. Tea polyphenols are widely considered as a kind of excellent antioxidant agents. It can be antioxidants by directly scavenging reactive oxide species or chelating transition metals, and indirectly upregulating the activity of antioxidant enzymes. In addition, tea polyphenols have also been observed a potent pro-oxidant capacity, which directly leads to the generation of reactive oxide species, and indirectly induces apoptosis and death of cancer cells. The underlying characters of its pro-oxidant activity in some diseases is not well understood. The present review we will discuss the dual character of tea polyphenols, both antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties, in some human diseases induced by oxidative stress.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; oxidative stress; pro-oxidant capacity; tea polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None.
Figures


References
-
- Graham HN. Green tea composition, consumption, and polyphenol chemistry. Prev Med. 1992;21:334–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-7435(92)90041-F - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stoner GD, Mukhtar H. Polyphenols as cancer chemopreventive agents. J Cell Biochem. 1995;59:169–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.240590822 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lambert JD, Elias RJ. The antioxidant and pro-oxidant activities of green tea polyphenols: a role in cancer prevention. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010;501:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2010.06.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frei B, Higdon JV. Antioxidant activity of tea polyphenols in vivo: evidence from animal studies. J Nutr. 2003;133:3275S–84S. - PubMed
-
- Yang CS, Lambert JD, Sang S. Antioxidative and anti-carcinogenic activities of tea polyphenols. Arch Toxicol. 2009;83:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0372-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

