PXR: More Than Just a Master Xenobiotic Receptor
- PMID: 29113993
- PMCID: PMC5767680
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.117.110155
PXR: More Than Just a Master Xenobiotic Receptor
Abstract
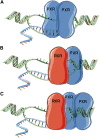
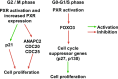
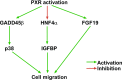
Pregnane X receptor (PXR) is a nuclear receptor considered to be a master xenobiotic receptor that coordinately regulates the expression of genes encoding drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters to essentially detoxify and eliminate xenobiotics and endotoxins from the body. In the past several years, the function of PXR in the regulation of xenobiotic metabolism has been extensively studied, and the role of PXR as a xenobiotic sensor has been well established. It is now clear, however, that PXR plays many other roles in addition to its xenobiotic-sensing function. For instance, recent studies have discovered previously unidentified roles of PXR in inflammatory response, cell proliferation, and cell migration. PXR also contributes to the dysregulation of these processes in diseases states. These recent discoveries of the role of PXR in the physiologic and pathophysiologic conditions of other cellular processes provides the possibility of novel targets for drug discovery. This review highlights areas of PXR regulation that require further clarification and summarizes the recent progress in our understanding of the nonxenobiotic functions of PXR that can be explored for relevant therapeutic applications.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad E, Rabbani G, Zaidi N, Khan MA, Qadeer A, Ishtikhar M, Singh S, Khan RH. (2013) Revisiting ligand-induced conformational changes in proteins: essence, advancements, implications and future challenges. J Biomol Struct Dyn 31:630–648. - PubMed
-
- Baert FJ, D’Haens GR, Peeters M, Hiele MI, Schaible TF, Shealy D, Geboes K, Rutgeerts PJ. (1999) Tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody (infliximab) therapy profoundly down-regulates the inflammation in Crohn’s ileocolitis. Gastroenterology 116:22–28. - PubMed
-
- Bailly-Maitre B, de Sousa G, Boulukos K, Gugenheim J, Rahmani R. (2001) Dexamethasone inhibits spontaneous apoptosis in primary cultures of human and rat hepatocytes via Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL induction. Cell Death Differ 8:279–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

