Using Smartphones to Help People with Intellectual and Sensory Disabilities Perform Daily Activities
- PMID: 29114539
- PMCID: PMC5660726
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00282
Using Smartphones to Help People with Intellectual and Sensory Disabilities Perform Daily Activities
Abstract
Background: People with mild-to-moderate intellectual disability and sensory impairments often fail to take initiative in starting and carrying out daily activities, with negative consequences for their occupational condition and social status. Their failure seems due to their inability to determine the right time for the activities and to remember all the activity steps.
Aim: This study assessed a smartphone intervention, which was designed to help eight participants (four presenting with intellectual disability and blindness and four presenting with intellectual disability and hearing impairment) to independently start and carry out daily activities at appropriate times.
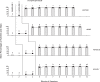
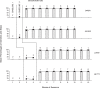
Method: The intervention was introduced according to a non-concurrent multiple baseline design across participants. During the intervention, each participant was provided with a smartphone, which was fitted with the time schedule of his or her activities and the verbal or pictorial instructions for the single steps of those activities. When the time for an activity was reached, the participant was automatically reminded to start that activity and, thereafter, he or she was presented with the instructions for it.
Results: The use of the smartphone intervention promoted great improvement over the baseline for all participants. That is, the participants managed to (a) independently start the activities at the scheduled times and (b) carry out those activities with high levels of accuracy.
Conclusion: A smartphone intervention, such as that used in this study, may help people with mild-to-moderate intellectual disability and sensory impairments to successfully engage in daily activities.
Keywords: activities; blindness; hearing impairment; intellectual disability; smartphone; technology.
Figures
References
-
- Channon A. Intellectual disability and activity engagement: exploring the literature from an occupational perspective. J Occup Sci (2014) 21:443–58. 10.1080/14427591.2013.829398 - DOI
-
- Duttlinger C, Ayres KM, Bevill-Davis A, Douglas KH. The effects of a picture activity schedule for students with intellectual disability to complete a sequence of tasks following verbal directions. Focus Autism Other Dev Disabil (2013) 28:32–43. 10.1177/1088357612460572 - DOI
-
- Gentry T, Lau S, Molinelli A, Fallen A, Kriner R. The Apple iPod as a vocational support aid for adults with autism: three case studies. J Vocat Rehabil (2012) 37:75–85. 10.3233/JVR-2012-0601 - DOI
-
- Mechling LC, Gast DL, Seid NH. Evaluation of a personal digital assistant as a self-prompting device for increasing multi-step task completion by students with moderate intellectual disabilities. Educ Train Autism Dev Disabil (2010) 45:422–39.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

