Potato starch synthases: Functions and relationships
- PMID: 29114568
- PMCID: PMC5637242
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.02.004
Potato starch synthases: Functions and relationships
Abstract
Starch, a very compact form of glucose units, is the most abundant form of storage polyglucan in nature. The starch synthesis pathway is among the central biochemical pathways, however, our understanding of this important pathway regarding genetic elements controlling this pathway, is still insufficient. Starch biosynthesis requires the action of several enzymes. Soluble starch synthases (SSs) are a group of key players in starch biosynthesis which have proven their impact on different aspects of the starch biosynthesis and functionalities. These enzymes have been studied in different plant species and organs in detail, however, there seem to be key differences among species regarding their contributions to the starch synthesis. In this review, we consider an update on various SSs with an emphasis on potato SSs as a model for storage organs. The genetics and regulatory mechanisms of potato starch synthases will be highlighted. Different aspects of various isoforms of SSs are also discussed.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Glycosyltransferase; Potato; Starch biosynthesis; Starch synthases.
Figures
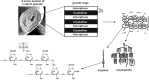
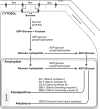
 and
and  represent putative transporters.
represent putative transporters.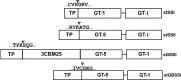

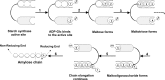
 : represent a glucose moiety with the reducing end.
: represent a glucose moiety with the reducing end.References
-
- Nazarian-Firouzabadi F., Kok-Jacon G., Vincken J.P., Ji Q., Suurs L.C.J.M., Visser R.G.F. Fusion proteins comprising the catalytic domain of mutansucrase and a starch-binding domain can alter the morphology of amylose-free potato starch granules during biosynthesis. Transgenic Res. 2007;16(5):645–656. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

