Integrative sparse principal component analysis of gene expression data
- PMID: 29114920
- PMCID: PMC5912177
- DOI: 10.1002/gepi.22089
Integrative sparse principal component analysis of gene expression data
Abstract
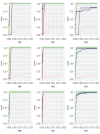
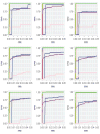
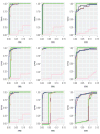
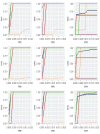
In the analysis of gene expression data, dimension reduction techniques have been extensively adopted. The most popular one is perhaps the PCA (principal component analysis). To generate more reliable and more interpretable results, the SPCA (sparse PCA) technique has been developed. With the "small sample size, high dimensionality" characteristic of gene expression data, the analysis results generated from a single dataset are often unsatisfactory. Under contexts other than dimension reduction, integrative analysis techniques, which jointly analyze the raw data of multiple independent datasets, have been developed and shown to outperform "classic" meta-analysis and other multidatasets techniques and single-dataset analysis. In this study, we conduct integrative analysis by developing the iSPCA (integrative SPCA) method. iSPCA achieves the selection and estimation of sparse loadings using a group penalty. To take advantage of the similarity across datasets and generate more accurate results, we further impose contrasted penalties. Different penalties are proposed to accommodate different data conditions. Extensive simulations show that iSPCA outperforms the alternatives under a wide spectrum of settings. The analysis of breast cancer and pancreatic cancer data further shows iSPCA's satisfactory performance.
Keywords: contrasted penalization; gene expression data; integrative analysis; sparse PCA.
© 2017 WILEY PERIODICALS, INC.
Figures
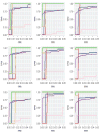
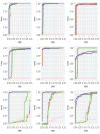
Similar articles
-
Integrative sparse partial least squares.Stat Med. 2021 Apr;40(9):2239-2256. doi: 10.1002/sim.8900. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Stat Med. 2021. PMID: 33559203 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting similarity of model sparsity structures in integrative analysis of cancer genetic data.Stat Med. 2017 Feb 10;36(3):509-559. doi: 10.1002/sim.7138. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Stat Med. 2017. PMID: 27667129 Free PMC article.
-
iSFun: an R package for integrative dimension reduction analysis.Bioinformatics. 2022 May 26;38(11):3134-3135. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac281. Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35441661 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Data Preprocessing on Integrative Matrix Factorization of Single Cell Data.Front Oncol. 2020 Jun 23;10:973. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00973. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32656082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sparse models for correlative and integrative analysis of imaging and genetic data.J Neurosci Methods. 2014 Nov 30;237:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 9. J Neurosci Methods. 2014. PMID: 25218561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prior information-assisted integrative analysis of multiple datasets.Bioinformatics. 2023 Aug 1;39(8):btad452. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad452. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37490475 Free PMC article.
-
Explainable machine learning approach for cancer prediction through binarilization of RNA sequencing data.PLoS One. 2024 May 10;19(5):e0302947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302947. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38728288 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual reality for the observation of oncology models (VROOM): immersive analytics for oncology patient cohorts.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 5;12(1):11337. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15548-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35790803 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of high-dimensional quantile regression with contrasted penalization.J Appl Stat. 2024 Dec 10;52(9):1760-1776. doi: 10.1080/02664763.2024.2438799. eCollection 2025. J Appl Stat. 2024. PMID: 40612015
-
Over-expression of mir-181a-3p in serum of breast cancer patients as diagnostic biomarker.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 27;51(1):372. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09272-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38411870
References
-
- Chiquet J, Grandvalet Y, Ambroise C. Inferring multiple graphical structures. Statistics and Computing. 2011;21:537–553.
-
- Gene expression omnibus. 2017 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/
-
- Grutzmann R, Boriss H, Ammerpohl O, Lttges J, Kalthoff H, Schackert HK, …Pilarsky C. Meta-analysis of microarray data on pancreatic cancer defines a set of commonly dysregulated genes. Oncogene. 2005;24:5079–5088. - PubMed
-
- Guerra R, Goldstein DR. Meta-analysis and combining information in genetics and genomics. CRC Press; 2009.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

