Polygonum multiflorm alleviates glucocorticoid‑induced osteoporosis and Wnt signaling pathway
- PMID: 29115514
- PMCID: PMC5780178
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7997
Polygonum multiflorm alleviates glucocorticoid‑induced osteoporosis and Wnt signaling pathway
Abstract
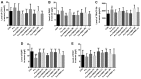
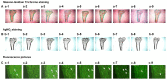
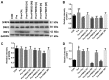
It is known that long‑term excessive administration of glucocorticoid (GC) results in osteoporosis. The present study aimed to evaluate the protective effects of Polygonum multiflorm (PM) on the bone tissue of rats with GC‑induced osteoporosis (GIO). A total of 90 6‑month‑old female Sprague Dawley rats (weight range, 190‑210 g) were randomly divided into nine groups: Control (normal saline); prednisone (GC; 6 mg·kg‑1·d‑1; Model); GC plus PMR30 (the 30% ethanol eluent fraction of PM) (H) (400 mg·kg‑1·d‑1); GC plus PMR30 (M) (200 mg·kg‑1·d‑1); GC plus PMR30 (L) (100 mg·kg‑1·d‑1); GC plus PMRF (fat‑soluble fraction of PM) (H) (400 mg·kg‑1·d‑1); GC plus PMRF (M) (200 mg·kg‑1·d‑1); GC plus PMRF (L) (100 mg·kg‑1·d‑1); GC plus calcitriol (CAL; 0.045 µg·kg‑1·d‑1; positive). Rats were administered intragastrically with prednisone and/or the aforementioned extracts for 120 days, and weighed once/week. The serum was collected for detection of biochemical markers. The left tibia was used for bone histomorphometry analysis. The right tibia was prepared for hematoxylin and eosin staining. The left femur was used to analyze the protein expression of dickkopf‑1 (DKK1), WNT inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1) and secreted frizzled related protein 4 using western blotting. Long‑term excessive treatment of prednisone inhibited the bone formation rate accompanied with a decrease in bone mass, growth plate, body weight, and the level of bone‑specific alkaline phosphatase and hydroxyl‑terminal propeptide of type I procollagen in the serum. Furthermore, a simultaneously increase in the level of tartrate resistant acid phosphatase‑5b and cross‑linked carboxy‑terminal telopeptide of type I collagen in the serum, in addition to DKK1, and WIF1 protein expression, was observed. PMR30 (M and L) and PMRF (H) groups were able to reduce the negative effects of GC on the bones. PMR30 (M and L) and PMRF (H) dose demonstrated a protective effect of PM on bone tissue in GIO rats. The mechanism underlying the preventive effect of PM for the treatment of GIO may be associated with direct upregulation of the canonical Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway.
Figures



References
-
- McLaughlin F, Mackintosh J, Hayes BP, McLaren A, Uings IJ, Salmon P, Humphreys J, Meldrum E, Farrow SN. Glucocorticoid-induced osteopenia in the mouse as assessed by histomorphometry, microcomputed tomography, and biochemical markers. Bone. 2002;30:924–930. doi: 10.1016/S8756-3282(02)00737-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

