The influence of dexamethasone on postoperative swelling and neurosensory disturbances after orthognathic surgery: a randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 29116013
- PMCID: PMC5678574
- DOI: 10.1186/s13005-017-0153-1
The influence of dexamethasone on postoperative swelling and neurosensory disturbances after orthognathic surgery: a randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Orthognathic surgery is associated with considerable swelling and neurosensory disturbances. Serious swelling can lead to great physical and psychological strain. A randomized, prospective, controlled clinical trial was realized in order to evaluate the effect of a preoperative intravenous dexamethasone injection of 40 mg on postoperative swelling and neurosensory disturbances after orthognathic surgery.
Methods: Thirty-eight patients (27 male and 11 female) patients, all with the indication for an orthognathic surgery, were enrolled in this study (mean age: 27.63 years, range: 16-61 years) and randomly divided into two groups (study group/ control group). Both groups underwent either maxillary and/or mandibular osteotomies, resulting in three subgroups according to surgical technique (A: LeFort I osteotomy, B: bilateral sagittal split osteotomy (BSSO), C: bimaxillary osteotomy). The study group received a single preoperative intravenous injection of 40 mg dexamethasone. Facial edema was measured by 3D surface scans on the 1st, 2nd, 5th, 14th and 90th postoperative day. Furthermore, neurosensory disturbances on the 2nd, 5th, 14th and 90th postoperative day were investigated by thermal stimulation.
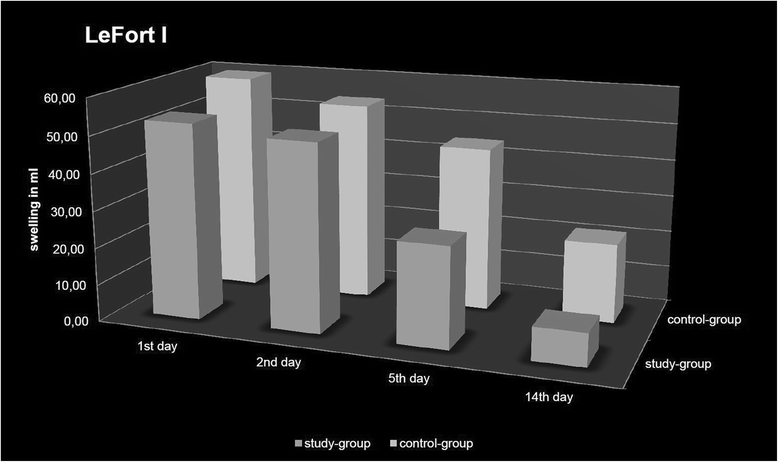
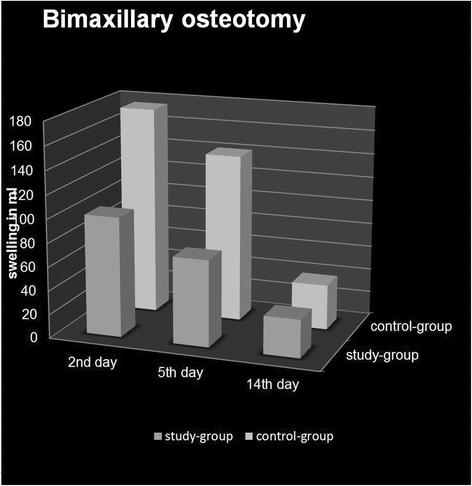
Results: Facial edema after LeFort I osteotomy, BSSO and bimaxillary osteotomy showed a significant decrease in the study group compared to the control group (P = 0.048, P = 0.045, P < 0.001). The influence of dexamethasone on neurosensory disturbances was not significant for the inferior alveolar nerve (P = 0.746) or the infraorbital nerve (P = 0.465).
Conclusions: Patients undergoing orthognathic surgery should receive a preoperative injection of dexamethasone in order to control and reduce edema. However, there was no influence of dexamethasone on reduction of neurosensory disturbances.
Trial registration: DRKS00009033 .
Keywords: Dexamethasone; Edema; Glucocorticoids; Neurosensory disturbance; Orthognathic surgery; Swelling.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Germany Protocol number: EK 4 / 14, Local ethics committee of the Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intravenous Dexamethasone Administration Before Orthognathic Surgery Reduces the Postoperative Edema of the Masseter Muscle: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Jun;75(6):1257-1262. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.12.048. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017. PMID: 28157491
-
Laser Biophotomodulation in Patients with Neurosensory Disturbance of the Inferior Alveolar Nerve After Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy: A 2-Year Follow-Up Study.Photomed Laser Surg. 2018 Jan;36(1):3-9. doi: 10.1089/pho.2017.4312. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Photomed Laser Surg. 2018. PMID: 29022844
-
Stellate Ganglion Block, Compared With Xenon Light Irradiation, Is a More Effective Treatment of Neurosensory Deficits Resulting From Orthognathic Surgery, as Measured by Current Perception Threshold.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015 Jul;73(7):1267-74. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2015.01.012. Epub 2015 Jan 24. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25900233
-
Facial nerve palsy following bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy for setback of the mandible.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011 Aug;40(8):884-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2011.02.030. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011. PMID: 21474283 Review.
-
Unilateral mydriasis after maxillary osteotomy: a case series and review of the literature.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015 Jun;73(6):1159-68. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2014.12.024. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25669129 Review.
Cited by
-
Piezo-osteotomy in orthognathic surgery: A comparative clinical study.Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2022 May-Aug;13(2):276-282. doi: 10.4103/njms.njms_357_21. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2022. PMID: 36051789 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive anaesthesia management strategies for orthognathic surgical procedure.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2025 Jan 1;30(1):e56-e64. doi: 10.4317/medoral.26833. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2025. PMID: 39396134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Prospective Randomized Study to Assess the Quality of Life in Post-Operative Recovery Phase in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Isolated Vertically Undisplaced Mandibular Parasymphysis Fracture Using Twin Mix Solution.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2022 Jun;21(2):413-419. doi: 10.1007/s12663-020-01471-3. Epub 2020 Oct 31. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2022. PMID: 35712384 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Influencing Clinical After Effects of Post Orthognathic Surgery - An Observational Clinical Study.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021 Jun;13(Suppl 1):S492-S495. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_728_20. Epub 2021 Jun 5. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021. PMID: 34447140 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation Therapy for Neurosensory Disturbances in Orthognathic Surgery Patients: A Systematic Review.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 16;15(1):111. doi: 10.3390/life15010111. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rana M, Gellrich N-C, von See C, Weiskopf C, Gerressen M, Ghassemi A, Modabber A. 3D evaluation of postoperative swelling in treatment of bilateral mandibular fractures using 2 different cooling therapy methods: a randomized observer blind prospective study. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg. 2013;41:e17–e23. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2012.04.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Widar F, Kashani H, Alsén B, Dahlin C, Rasmusson L. The effects of steroids in preventing facial oedema, pain, and neurosensory disturbances after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44:252–258. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2014.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

