PRENACEL - a mHealth messaging system to complement antenatal care: a cluster randomized trial
- PMID: 29116028
- PMCID: PMC5678588
- DOI: 10.1186/s12978-017-0407-1
PRENACEL - a mHealth messaging system to complement antenatal care: a cluster randomized trial
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to determine whether PRENACEL (a bi-directional, mobile-phone based, short text message service (SMS)) increases the coverage of recommended antenatal care (ANC) practices.
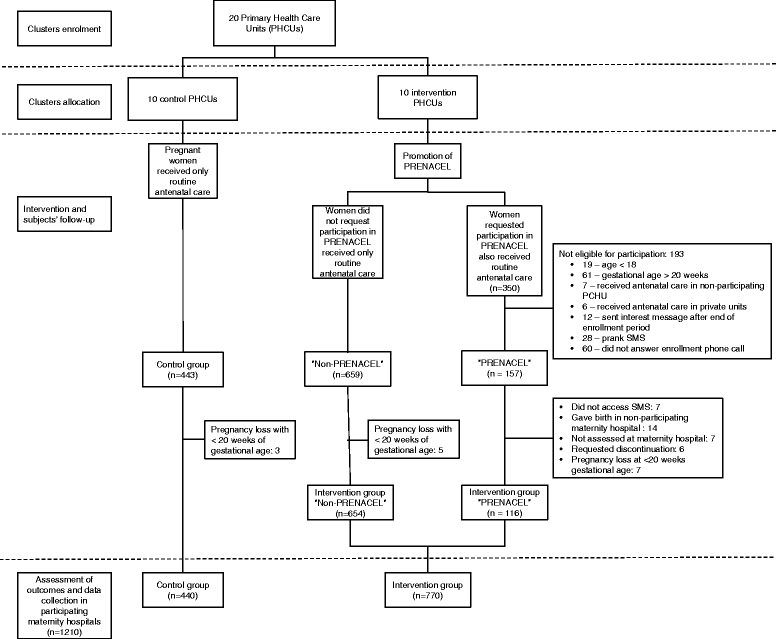
Methods: A parallel, cluster-randomized trial in which 20 public primary Health Care Units (PHCUs) were randomly allocated to the intervention (10 PHCUs) or control (10 PHCUs) group. The study population included pregnant women aged 18 or above with a gestational age of 20 weeks or less. Pregnant women receiving ANC in intervention PHCUs were invited through leaflets and posters to register in PRENACEL. Women who registered in PRENACEL received a weekly set of short text messages with health education and health promotion content related to pregnancy and childbirth and were also able to clarify ANC queries through SMS. All women received routine ANC. The primary outcome was the proportion of women with high ANC Score, a composite measure of coverage of recommended ANC practices. Chi-square or Fisher's exact tests and multivariate log-binomial regression were used to analyze the outcomes.
Results: A total of 1210 eligible women received ANC in the participating PHCUs and took part of this study (770 in the intervention group and 440 in the control group). 20.4% (157/770) of intervention-group women registered in PRENACEL, but only 116 read all messages (73.9% of women who registered in PRENACEL, 116/157). The adjusted intention-to-treat analysis suggested no difference between intervention and control groups in the primary outcome (Adjusted Relative Risk (AdjRR): 1.05 (95% Confidence Interval (CI): 1.00-1.09). Both crude and adjusted per-protocol analysis suggested a positive effect of PRENACEL (Crude RR (95% CI): 1.14 (1.06-1.22), AdjRR (95% CI): 1.12 (1.05-1.21). The multivariate analysis also suggests that the PRENACEL group (women who read all SMS) had higher mean ANC score [48.5 (±4.2) vs 45.2 (±8.7), p < 0.01], higher proportion of women with ≥6 ANC visits (96.9% vs. 84.8%, p = 0.01), and higher rates of syphilis testing (40.5% vs. 24.8%, p = 0.03) and HIV testing (46.6% vs. 25.7%, p < 0.01) during ANC.
Conclusions: A bi-directional, mobile-phone based, short text message service is potentially useful to improve the coverage of recommended ANC practices, including syphilis and HIV testing.
Trial registration: Clinical trial registry: RBR-54zf73 , U1111-1163-7761.
Resumo: Introdução: O objetivo deste estudo foi determinar se o PRENACEL, um serviço bidirecional de mensagens curtas de texto (SMS) com base na telefonia celular, aumenta a cobertura das práticas recomendadas de cuidados pré-natais (PN).
Métodos: um ensaio paralelo, aleatorizado por conglomerados, no qual 20 unidades básicas de saúde (UBS) foram alocadas aleatoriamente para o grupo de intervenção (10 UBS) ou controle (10 UBS). A população estudada incluiu gestantes com idade igual ou superior a 18 anos com idade gestacional de 20 semanas ou menos. As gestantes que receberam PN em UBS intervenção foram convidadas através de folhetos e cartazes para se inscreverem no PRENACEL. As mulheres que se registraram no PRENACEL receberam um conjunto semanal de SMS com conteúdo de educação e promoção da saúde relacionadas à gravidez e parto e também puderam esclarecer dúvidas relacionadas ao PN através de SMS. Todas as mulheres receberam PN de rotina. O desfecho primário foi a proporção de mulheres com um alto escore de PN, uma medida da cobertura das principais práticas recomendadas no PN.
Resultados: um total de 1.210 mulheres participaram deste estudo (770 no grupo de intervenção e 440 no grupo de controle). 20,4% (157/770) das mulheres do grupo de intervenção demonstraram interesse e foram registradas no PRENACEL, mas apenas 116 leram as mensagens (73,9%, 116/157). A análise ajustada de intenção de tratamento sugeriu ausência de efeito da intervenção no desfecho primário (Risco Relativo (RR) ajustado: 1,05, Intervalo de Confiança (IC) de 95%: 1,00-1,09). A análise por protocolo sugeriu um efeito positivo do PRENACEL [RR bruto (IC 95%): 1,14 (1,06-1,22), RR ajustado (IC 95%): 1,12 (1,05-1,21)]. A análise multivariada sugeriu que as mulheres que leram os SMS apresentaram a maior média do escore de PN [48,5 (±4,2) vs 45,2 (±8,7), p < 0,01], maior proporção de mulheres com ≥6 consultas (96,9% vs. 84,8%, p = 0,01) e maiores taxas de teste de sífilis (40,5% vs. 24,8%, p = 0,03) e HIV (46,6% vs. 25,7%, p < 0,01) durante o PN.
Conclusões: o sistema PRENACEL é potencialmente útil para melhorar a cobertura das práticas recomendadas de PN, incluindo testes de sífilis e HIV.
Keywords: Adherence; Antenatal; Pregnancy; Syphilis; Text messaging; mHealth.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the institutional review board of Centro de Saúde Escola Joel Domingos Machado, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil, under protocol # 971.458 on March 3, 2015. This study obtained all required authorizations and the relevant consent to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors reviewed the study, and approved the final version for publication.
Competing interests
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
-
- United Nations. Sustainable development goals. [Internet]. 2015. Available from: http://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/
-
- Brazil . [Negociações da agenda de desenvolvimento pós-2015: elementos orientadores da posição brasileira].[Internet] 2015. Negotiating the post-2015 development agenda: guiding principles of the Brazilian position.
-
- WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group and the United Nations Population Division. Trends in maternal mortality: 1990 to 2015 Estimates by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group and the United Nations Population Division. 2015, WHO/RHR/15.23. Available at http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/194254/1/9789241565141_eng.pdf?...
-
- Miller S, Abalos E, Chamillard M, Ciapponi A, Colaci D, Comandé D, Diaz V, Geller S, Hanson C, Langer A, Manuelli V, Millar K, Morhason-Bello I, Castro CP, Pileggi VN, Robinson N, Skaer M, Souza JP, Vogel JP, Althabe F. Beyond too little, too late and too much, too soon: a pathway towards evidence-based, respectful maternity care worldwide. Lancet. 2016;388(10056):2176–2192. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31472-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical