CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010-2014
- PMID: 29117289
- PMCID: PMC5693142
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nox158
CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010-2014
Figures










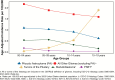



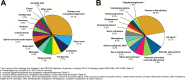
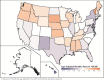
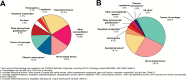

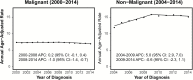
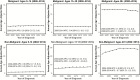

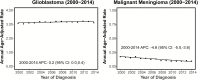
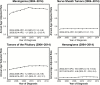
References
-
- Louis D, Wiestler O, Cavanee W, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2007.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National Program of Cancer Registries Cancer Surveillance System Rationale and Approach 1999; http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/npcr/pdf/npcr_css.pdf.
-
- Wiśniewski JR, Zougman A, Nagaraj N, Mann M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat Methods. 2009;6(5):359–362. - PubMed
-
- Benign Brain Tumor Cancer Registries Amendment Act, 107th Cong. § 260 (2002) http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/PLAW-107publ260/pdf/PLAW-107publ260.pdf.

