Estimates of the Burden of Group B Streptococcal Disease Worldwide for Pregnant Women, Stillbirths, and Children
- PMID: 29117332
- PMCID: PMC5849940
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cix664
Estimates of the Burden of Group B Streptococcal Disease Worldwide for Pregnant Women, Stillbirths, and Children
Abstract
Background: We aimed to provide the first comprehensive estimates of the burden of group B Streptococcus (GBS), including invasive disease in pregnant and postpartum women, fetal infection/stillbirth, and infants. Intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis is the current mainstay of prevention, reducing early-onset infant disease in high-income contexts. Maternal GBS vaccines are in development.
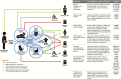
Methods: For 2015 live births, we used a compartmental model to estimate (1) exposure to maternal GBS colonization, (2) cases of infant invasive GBS disease, (3) deaths, and (4) disabilities. We applied incidence or prevalence data to estimate cases of maternal and fetal infection/stillbirth, and infants with invasive GBS disease presenting with neonatal encephalopathy. We applied risk ratios to estimate numbers of preterm births attributable to GBS. Uncertainty was also estimated.
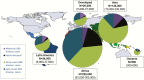
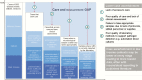
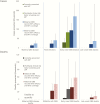
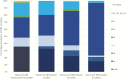
Results: Worldwide in 2015, we estimated 205000 (uncertainty range [UR], 101000-327000) infants with early-onset disease and 114000 (UR, 44000-326000) with late-onset disease, of whom a minimum of 7000 (UR, 0-19000) presented with neonatal encephalopathy. There were 90000 (UR, 36000-169000) deaths in infants <3 months age, and, at least 10000 (UR, 3000-27000) children with disability each year. There were 33000 (UR, 13000-52000) cases of invasive GBS disease in pregnant or postpartum women, and 57000 (UR, 12000-104000) fetal infections/stillbirths. Up to 3.5 million preterm births may be attributable to GBS. Africa accounted for 54% of estimated cases and 65% of all fetal/infant deaths. A maternal vaccine with 80% efficacy and 90% coverage could prevent 107000 (UR, 20000-198000) stillbirths and infant deaths.
Conclusions: Our conservative estimates suggest that GBS is a leading contributor to adverse maternal and newborn outcomes, with at least 409000 (UR, 144000-573000) maternal/fetal/infant cases and 147000 (UR, 47000-273000) stillbirths and infant deaths annually. An effective GBS vaccine could reduce disease in the mother, the fetus, and the infant.
Keywords: group B Streptococcus; infection; maternal; newborn; stillbirth.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures




References
-
- Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D et al. . Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000-13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015; 385:430–40. - PubMed
-
- Blencowe H, Cousens S, Jassir FB et al. . National, regional, and worldwide estimates of stillbirth rates in 2015, with trends from 2000: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2016; 4: e98–108. - PubMed
-
- Lawn JE, Blencowe H, Oza S et al. . Every Newborn: progress, priorities, and potential beyond survival. Lancet 2014. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61345–8. - PubMed
-
- Graham W, Woodd S, Byass P et al. . Diversity and divergence: the dynamic burden of poor maternal health. Lancet 2016; 388:2164–75. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R et al. . Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2013; 380: 2197–223. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

