Alzheimer's Disease-Related Dementias Summit 2016: National research priorities
- PMID: 29117955
- PMCID: PMC5719928
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004717
Alzheimer's Disease-Related Dementias Summit 2016: National research priorities
Abstract
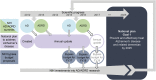
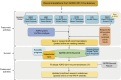
Goal 1 of the National Plan to Address Alzheimer's Disease is to prevent and effectively treat Alzheimer disease and Alzheimer disease-related dementias by 2025. To help inform the research agenda toward achieving this goal, the NIH hosts periodic summits that set and refine relevant research priorities for the subsequent 5 to 10 years. This proceedings article summarizes the 2016 Alzheimer's Disease-Related Dementias Summit, including discussion of scientific progress, challenges, and opportunities in major areas of dementia research, including mixed-etiology dementias, Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal degeneration, vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia, dementia disparities, and dementia nomenclature.
© 2017 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Dementia: Fact Sheet N°362 [online]. Available at: who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/. Accessed August 2, 2017.
-
- Bachman DL, Wolf PA, Linn RT, et al. Incidence of dementia and probable Alzheimer's disease in a general population: the Framingham Study. Neurology 1993;43:515–519. - PubMed
-
- Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Beckett LA, et al. Age-specific incidence of Alzheimer's disease in a community population. JAMA 1995;273:1354–1359. - PubMed
-
- Kawas C, Gray S, Brookmeyer R, Fozard J, Zonderman A. Age-specific incidence rates of Alzheimer's disease: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Neurology 2000;54:2072–2077. - PubMed
-
- Kukull WA, Higdon R, Bowen JD, et al. Dementia and Alzheimer disease incidence: a prospective cohort study. Arch Neurol 2002;59:1737–1746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
