Structure-based drug design: aiming for a perfect fit
- PMID: 29118091
- PMCID: PMC5869280
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20170052
Structure-based drug design: aiming for a perfect fit
Abstract
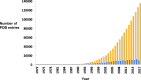
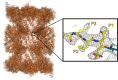
Knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of therapeutically relevant targets has informed drug discovery since the first protein structures were determined using X-ray crystallography in the 1950s and 1960s. In this editorial we provide a brief overview of the powerful impact of structure-based drug design (SBDD), which has its roots in computational and structural biology, with major contributions from both academia and industry. We describe advances in the application of SBDD for integral membrane protein targets that have traditionally proved very challenging. We emphasize the major progress made in fragment-based approaches for which success has been exemplified by over 30 clinical drug candidates and importantly three FDA-approved drugs in oncology. We summarize the articles in this issue that provide an excellent snapshot of the current state of the field of SBDD and fragment-based drug design and which offer key insights into exciting new developments, such as the X-ray free-electron laser technology, cryo-electron microscopy, open science approaches and targeted protein degradation. We stress the value of SBDD in the design of high-quality chemical tools that are used to interrogate biology and disease pathology, and to inform target validation. We emphasize the need to maintain the scientific rigour that has been traditionally associated with structural biology and extend this to other methods used in drug discovery. This is particularly important because the quality and robustness of any form of contributory data determines its usefulness in accelerating drug design, and therefore ultimately in providing patient benefit.
Keywords: drug discovery and design; pharmacology; structure.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are employees of The Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) which has research collaborations with a range of commercial partners for which employees as well as ICR may benefit. R.v.M. is a former employee of Astex Pharmaceuticals and P.W. is a former employee of AstraZeneca.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas S.E., Mendes V., Kim S.Y., Malhotra S., Ochoa-Montano B., Blaszczyk M. et al. (2017) Structural biology and the design of new therapeutics: from HIV and cancer to mycobacterial infections: a paper dedicated to John Kendrew. J. Mol. Biol. 429, 2677–2693 - PubMed
-
- Perutz M.F., Rosa J. and Schechter A. (1978) Therapeutic agents for sickle cell disease. Nature 275, 369–370 - PubMed
-
- Navia M.A., Fitzgerald P.M., McKeever B.M., Leu C.T., Heimbach J.C., Herber W.K et al. (1989) Three-dimensional structure of aspartyl protease from human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1. Nature 337, 615–620 - PubMed
-
- Blundell T. and Pearl L. (1989) Retroviral proteinases. A second front against AIDS. Nature 337, 596–597 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

