Nonhuman Primate Optogenetics: Recent Advances and Future Directions
- PMID: 29118219
- PMCID: PMC5678022
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1839-17.2017
Nonhuman Primate Optogenetics: Recent Advances and Future Directions
Abstract
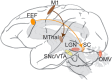
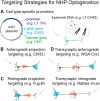
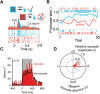
Optogenetics is the use of genetically coded, light-gated ion channels or pumps (opsins) for millisecond resolution control of neural activity. By targeting opsin expression to specific cell types and neuronal pathways, optogenetics can expand our understanding of the neural basis of normal and pathological behavior. To maximize the potential of optogenetics to study human cognition and behavior, optogenetics should be applied to the study of nonhuman primates (NHPs). The homology between NHPs and humans makes these animals the best experimental model for understanding human brain function and dysfunction. Moreover, for genetic tools to have translational promise, their use must be demonstrated effectively in large, wild-type animals such as Rhesus macaques. Here, we review recent advances in primate optogenetics. We highlight the technical hurdles that have been cleared, challenges that remain, and summarize how optogenetic experiments are expanding our understanding of primate brain function.
Keywords: NHP; monkey; opsins; optogenetic; optrode; promoter.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/3710894-10$15.00/0.
Figures

References
-
- Bankiewicz KS, Eberling JL, Kohutnicka M, Jagust W, Pivirotto P, Bringas J, Cunningham J, Budinger TF, Harvey-White J (2000) Convection-enhanced delivery of AAV vector in parkinsonian monkeys; in vivo detection of gene expression and restoration of dopaminergic function using pro-drug approach. Exp Neurol 164:2–14. 10.1006/exnr.2000.7408 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
