Decreased absolute numbers of CD3+ T cells and CD8+ T cells during aging in herpes zoster patients
- PMID: 29118328
- PMCID: PMC5678144
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15390-w
Decreased absolute numbers of CD3+ T cells and CD8+ T cells during aging in herpes zoster patients
Abstract
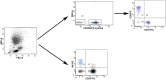
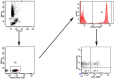
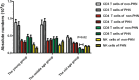
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an infectious dermatosis with high incidence worldwide. Age is a key risk factor for HZ, and postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is the main sequelae. Until now, no index has been available to predict the pathogenesis of PHN, and rare reports have focused on the immune response during aging and PHN. In this study, we selected immunoglobulin and complement proteins as markers for humoral immunity, while T lymphocyte subsets and natural killer (NK) cells were selected as markers for cell immunity, to systematically study the characteristics of immune responses in the peripheral blood of HZ patients. Our data showed that the absolute number of CD3+ T cells and CD8+ T cells decreased during aging and PHN. This implies that more attention should be paid to prevent the occurrence of PHN, especially in the aged population.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
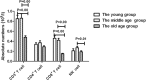

References
-
- Arvin, A. M. Varicella-zoster virus. Fields virology (4th edition) edn, 2731–2768 (Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, 2001).
-
- S. E., Cohen, J. & Straus. Varicella zoster virus and its replication. Fields virology. (4th edition). edn, 2707–2730 (Raven Press, 2001).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

