Genome-wide Association Study of Idiopathic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head
- PMID: 29118346
- PMCID: PMC5678103
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-14778-y
Genome-wide Association Study of Idiopathic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head
Abstract
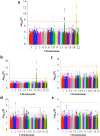
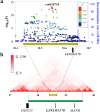
Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head (IONFH) is an ischemic disorder that causes bone necrosis of the femoral head, resulting in hip joint dysfunction. IONFH is a polygenic disease and steroid and alcohol have already known to increase its risk; however, the mechanism of IONFH remains to be elucidated. We performed a genome-wide association study using ~60,000 subjects and found two novel loci on chromosome 20q12 and 12q24. Big data analyses identified LINC01370 as a candidate susceptibility gene in the 20q12 locus. Stratified analysis by IONFH risk factors suggested that the 12q24 locus was associated with IONFH through drinking capacity. Our findings would shed new light on pathophysiology of IONFH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling of hip articular cartilage identifies differentially methylated loci associated with osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Bone. 2019 Oct;127:296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.06.021. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Bone. 2019. PMID: 31233934
-
Novel susceptibility loci for steroid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus.Hum Mol Genet. 2022 Mar 31;31(7):1082-1095. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab306. Hum Mol Genet. 2022. PMID: 34850884 Free PMC article.
-
Free vascularized fibular grafting for the treatment of postcollapse osteonecrosis of the femoral head.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003 Jun;85(6):987-93. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200306000-00001. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. PMID: 12783992
-
Association of eNOS polymorphisms with susceptibility to osteonecrosis of the femur head : A meta-analysis.Z Rheumatol. 2017 Apr;76(3):267-273. doi: 10.1007/s00393-016-0093-3. Z Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27312465 Review. English.
-
[Coxarthrosis secondary to ischemic necrosis of the femoral head in Cushing's disease].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1991;77(5):362-5. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1991. PMID: 1836890 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Gut Microbiota-Derived Butyric Acid Alleviates Glucocorticoid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head via Modulating Inflammatory Cytokines in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 Jun 5;2025:8742817. doi: 10.1155/mi/8742817. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40510588 Free PMC article.
-
The bibliometric and visualization analysis of alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: research trends and future directions (1998-2024).J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Aug 2;20(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-06138-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40753253 Free PMC article.
-
Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head.J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 May 1;6(5):e21.00176. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00176. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 35511598 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray profiling of circular RNAs in steroid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(10):e19465. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019465. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32150104 Free PMC article.
-
[Atraumatic necrosis of the femoral head].Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2025 Jun 26. doi: 10.1007/s00132-025-04666-z. Online ahead of print. Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40569425 German.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

