Intraparotid Schwannoma Masquerading as Primary Spindle Cell Tumour of Parotid: A Diagnostic Pitfall
- PMID: 29118479
- PMCID: PMC5655661
- DOI: 10.4103/JOC.JOC_147_15
Intraparotid Schwannoma Masquerading as Primary Spindle Cell Tumour of Parotid: A Diagnostic Pitfall
Abstract
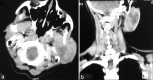
A middle-aged female presented with a painless, slowly growing mass in the left parotid region; fine needle aspiration cytology from the mass showed uniform spindle cells in a fibrillary background with some cells showing palisading. A cytodiagnosis of schwannoma was given, which was further confirmed on biopsy.
Keywords: Nerve sheath tumor; parotid neurilemmoma; salivary gland schwanomma.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Balle VH, Greisen O. Neurilemomas of the facial nerve presenting as parotid tumors. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1984;93:70–2. - PubMed
-
- Chiang CW, Chang YL, Lou PJ. Multicentricity of intraparotid facial nerve schwannomas. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001;110:871–4. - PubMed
-
- Enzinger FM, Weiss SW. Soft tissue tumors. 3rd edition. St. Louis, CV: Mosby; 1996. pp. 1146–50.
-
- Maly B, Maly A, Doviner V, Reinhartz T, Sherman Y. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of intraparotid schwannoma: A case report. Acta Cytol. 2003;47:1131–4. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Borkataky S, Agarwal R, Agarwal R, Singh S, Gupta K, et al. Rare diagnosis on aspiration of parotid gland Schwannoma. Acta Cytol. 2010;54:112–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

