Revision of torrent mites (Parasitengona, Torrenticolidae, Torrenticola) of the United States and Canada: 90 descriptions, molecular phylogenetics, and a key to species
- PMID: 29118596
- PMCID: PMC5674090
- DOI: 10.3897/zookeys.701.13261
Revision of torrent mites (Parasitengona, Torrenticolidae, Torrenticola) of the United States and Canada: 90 descriptions, molecular phylogenetics, and a key to species
Abstract
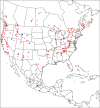
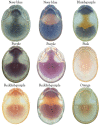
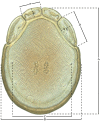
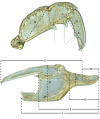
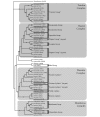
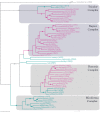
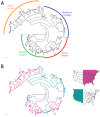
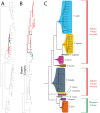
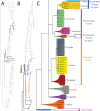
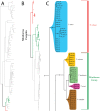
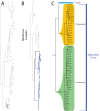
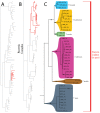
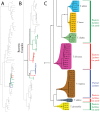
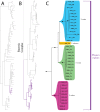
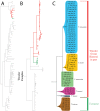
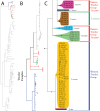
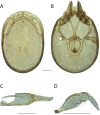
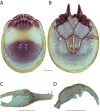
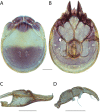
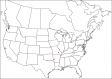
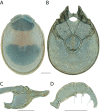
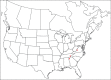
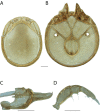
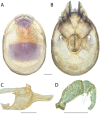
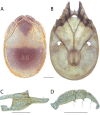
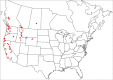
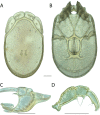
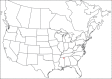
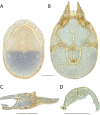
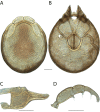
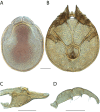
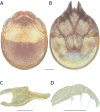
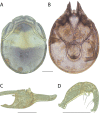
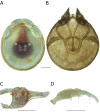
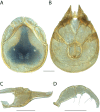
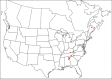
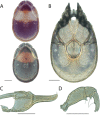
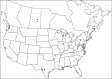
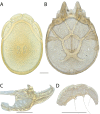
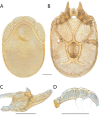
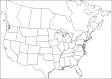
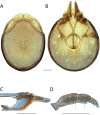
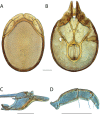
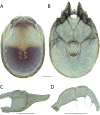
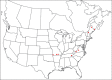
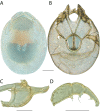
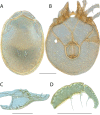
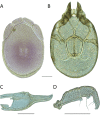
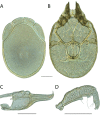
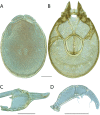
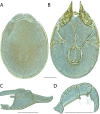
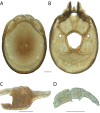
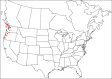
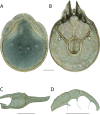
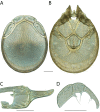
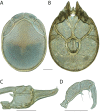
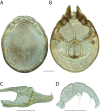
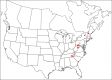
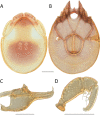
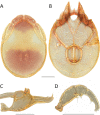
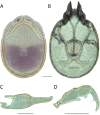
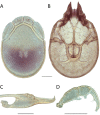
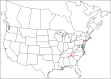
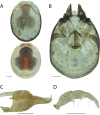
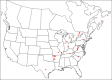
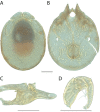
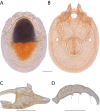
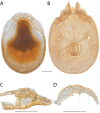
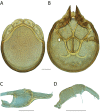
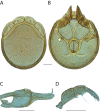
The descriptive biology of torrent mites (Parasitengona: Torrenticolidae: Torrenticola) of North America (north of Mexico) is investigated using integrative methods. Material examined includes approximately 2,300 specimens from nearly 500 localities across the United States and Canada, and a few collections in Mexico and Central America. Species hypotheses are derived from a phylogenetic analysis of the barcoding region of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (COI) for 476 specimens and supported with morphology and biogeography. Relationships between species are examined with a combined analysis of COI and two expansion regions (D2-3) of the large ribosomal subunit (28S rDNA) for 57 specimens. All previously described species from the US and Canada are examined. Our results indicate the need to synonymize four species: T. mercedensis (Marshall, 1943) is a junior synonym of T. sierrensis (Marshall, 1943); T. rectiforma Habeeb, 1974 is a junior synonym of T. ellipsoidalis (Marshall, 1943); T. neoconnexa Habeeb, 1957 is a junior synonym of T. magnexa Habeeb, 1955; and T. esbelta Cramer, 1992 is a junior synonym of T. boettgeri KO Viets, 1977. We describe 66 new species and re-describe all previously described regional species. Our findings indicate that total diversity of Torrenticola in the United States and Canada comprises 90 species, 57 known from the east and 33 from the west. We organize these species into four species complexes that include 13 identification groups. An additional 13 species do not fit within an identification group. The southern Appalachians are suspected to contain the highest concentration of remaining undescribed diversity. A key is provided to all known species in the US and Canada.
Keywords: Acari; Acariformes; Hydrachnidiae; integrative taxonomy; turbo-taxonomy; water mites.
Figures

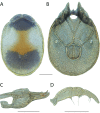
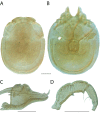

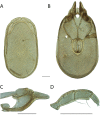
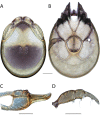
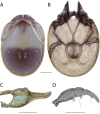
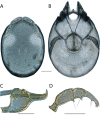
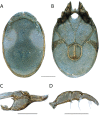
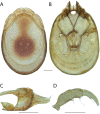
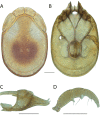
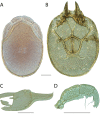
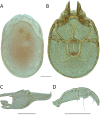
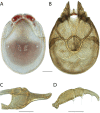
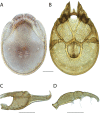
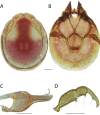
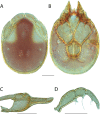
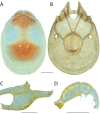
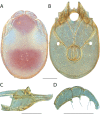
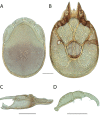
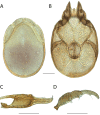
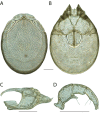
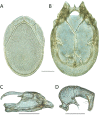

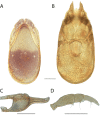
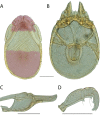
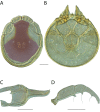
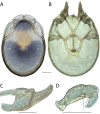
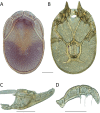
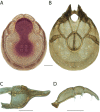
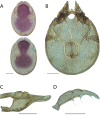
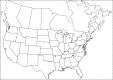
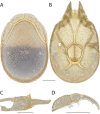
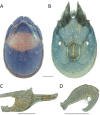
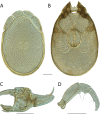
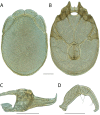
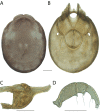
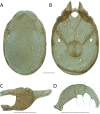
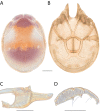
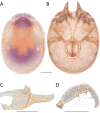
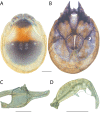
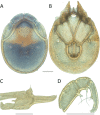
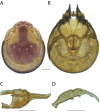
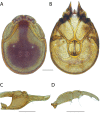
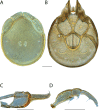
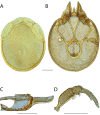
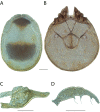
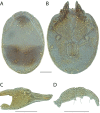
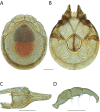
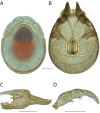
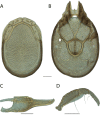
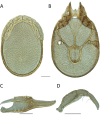
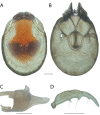
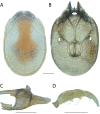
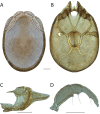
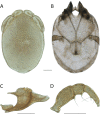
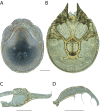
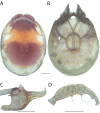
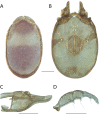
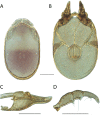
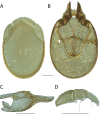
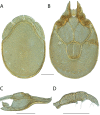
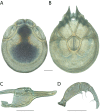
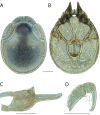
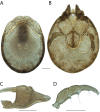
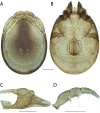
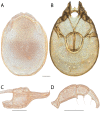
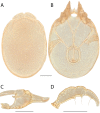
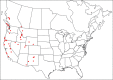
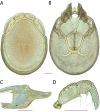
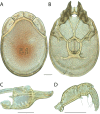
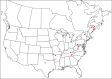
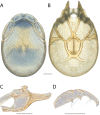
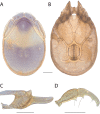
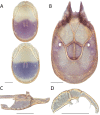
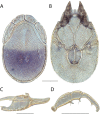
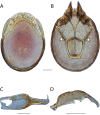
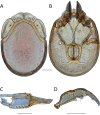
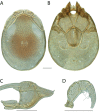
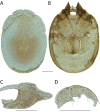
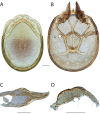
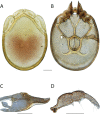
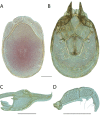
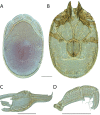
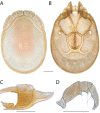
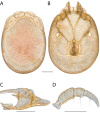
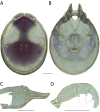
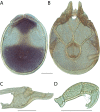
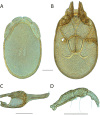
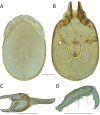
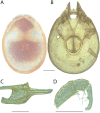
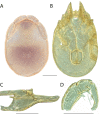
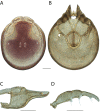

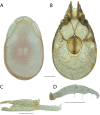
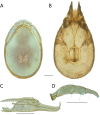
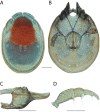
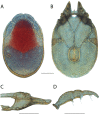
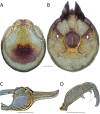
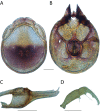
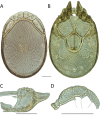
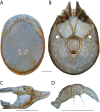
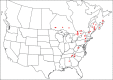
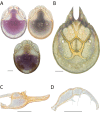
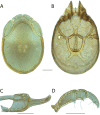
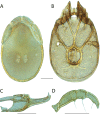
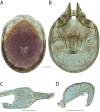
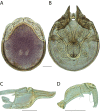
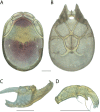
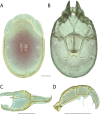
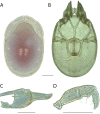
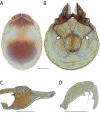

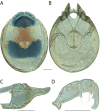
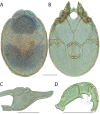
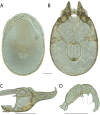
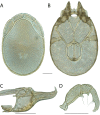
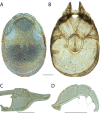
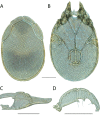
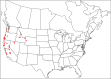
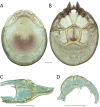
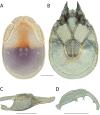
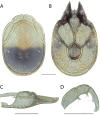
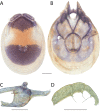
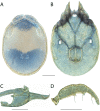

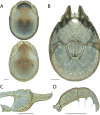
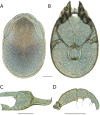
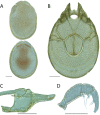
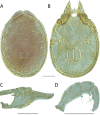
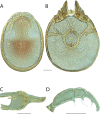
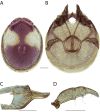
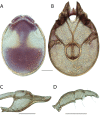
References
-
- Cherri CR, Fisher JR, Dowling APG. (2016) The masked torrent mite, Torrenticola larvata sp. n. (Acari: Hydrachnidiae: Torrenticolidae): a water mite endemic to the Ouachita Mountains of North America. Acarologia 56: 245–256. - DOI
-
- Conroy JC. (1968) The water-mites of Western Canada. National Museums of Canada Bulletin 223: 23–43.
-
- Conroy JC, Scudder GGE. (1975) An annotated checklist of the water mites (Acari) of British Columbia. Syesis 8: 305–310.
-
- Cook DR. (1980) Studies on neotropical water mites. Memoirs of the American Entomological Institute 31: 49–397.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
