DDX3 binding with CK1ε was closely related to motor neuron degeneration of ALS by affecting neurite outgrowth
- PMID: 29118923
- PMCID: PMC5666070
DDX3 binding with CK1ε was closely related to motor neuron degeneration of ALS by affecting neurite outgrowth
Abstract
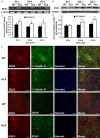
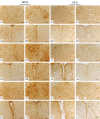
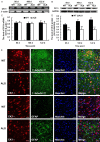
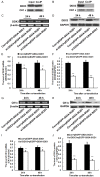
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a chronic neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive degeneration of motor neurons. The pathogenesis of ALS remains largely unknown. RNA helicase DDX3 is a multifunctional protein involved in several steps of gene expression. Casein kinase 1ε (CK1ε) is an important signal molecule of Wnt signaling pathway and is closely related to neurite growth. However, the roles of DDX3 and CK1ε in the pathogenesis of ALS remain unclear. In this study, we first investigated the expression of DDX3 and CK1ε in the spinal cord of SOD1-G93A ALS transgenic mice using RT-PCR, Western blot and immunohistochemical technique. Results showed that the altered expression of DDX3 and CK1ε was found in the spinal cord of ALS mice. DDX3 and CK1ε positive cells were mainly distributed in the anterior horn of spinal cord and co-localized with neurons not with glial cells, suggesting that the altered expression of DDX3 and CK1ε was closely related to motor neuron degeneration of ALS. Moreover, we selected NSC34 cell line and transfected pEGFP-G93A-SOD1 plasmid to further examine the mechanism. Knockdown of DDX3 that uses small interfering RNA (siRNA) decreased the mRNA and protein levels of CK1ε significantly and inhibited neurite outgrowth of SOD1 mutant NSC34 cells in vitro. Co-immunoprecipitation kit confirmed that DDX3 could band with CK1ε in vivo. Our data suggested that DDX3 binding with CK1ε was closely related to motor neuron degeneration of ALS by affecting neurite outgrowth. Thus, elucidating the underlying mechanisms of ALS is crucial for future development of ALS treatments.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; CK1ε; DDX3; NSC34 cells; SOD1-G93A transgenic mice.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Sirianni AC, Jiang J, Zeng J, Mao LL, Zhou S, Sugarbaker P, Zhang X, Li W, Friedlander RM, Wang X. N-acetyl-l-tryptophan, but not N-acetyl-d-tryptophan, rescues neuronal cell death in models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem. 2015;134:956–968. - PubMed
-
- Turner MR, Hardiman O, Benatar M, Brooks BR, Chio A, de Carvalho M, Ince PG, Lin C, Miller RG, Mitsumoto H, Nicholson G, Ravits J, Shaw PJ, Swash M, Talbot K, Traynor BJ, Van den Berg LH, Veldink JH, Vucic S, Kiernan MC. Controversies and priorities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:310–322. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY, Dal Canto MC, Polchow CY, Alexander DD, Caliendo J, Hentati A, Kwon YW, Deng HX, et al. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science. 1994;264:1772–1775. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
