Combination of EZH2 inhibitor and BET inhibitor for treatment of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
- PMID: 29118968
- PMCID: PMC5663148
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-017-0184-0
Combination of EZH2 inhibitor and BET inhibitor for treatment of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
Abstract
Background: Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma is an infiltrative, often high-grade glioma of the brainstem that is not amenable to surgical resection. The current treatment of DIPG by radiation therapy showed dramatically improvement of patient's condition, however, the tumor recurs rapidly. More and more studies are focused on the genetic and epigenetic drivers of DIPGs, which may provide more and more novel therapy target for DIPG. EZH2 has been proved to be a potential therapeutic target for H3K27M-mutant pediatric gliomas recently. Meanwhile, BET family protein is a hot target in many different types of cancers, including DIPG. In this study, we performed the treatment of both EZH2 and BET inhibitor for DIPG cells.
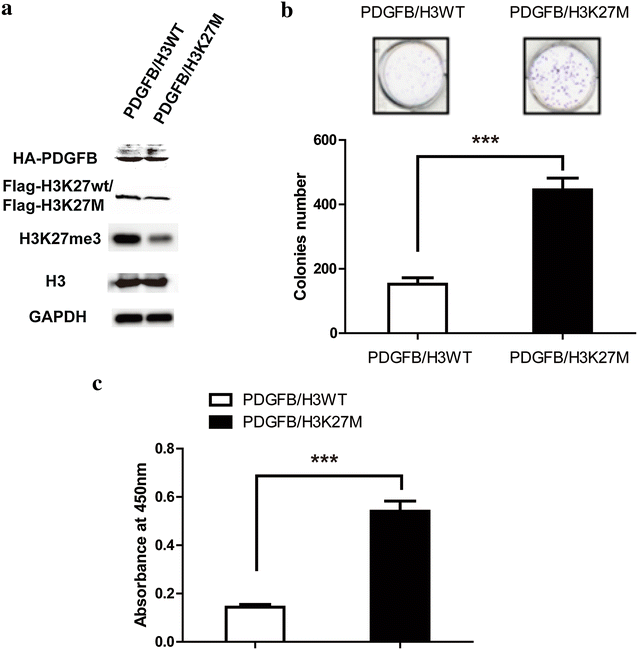
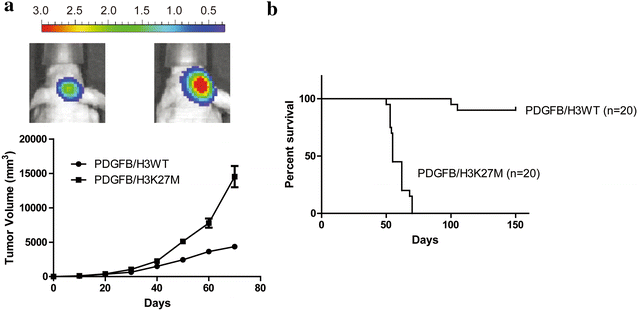
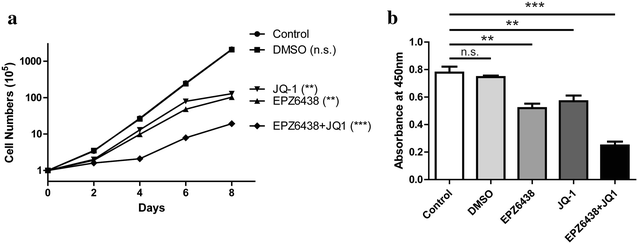
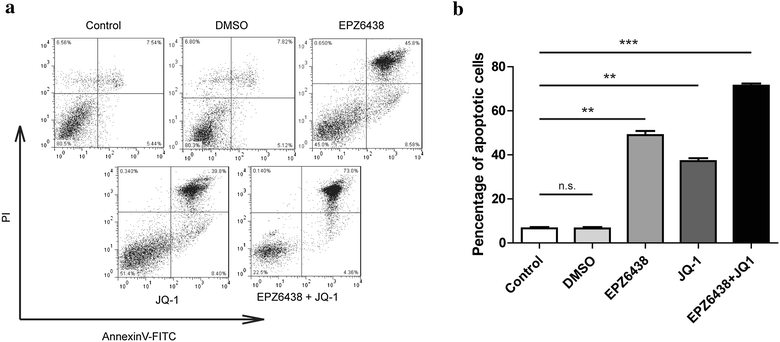
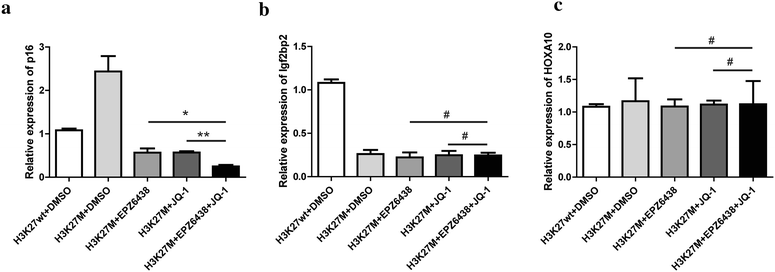
Results: The combination of these two inhibitors exhibited better inhibition of the tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo compared to use the inhibitor individually. This inhibition was performed by blocking the proliferation and promoting the cell apoptosis. Meanwhile, combination treatment of these two inhibitors would also affect the epigenetic markers which were abnormal in the tumors of the certain set of genes.
Conclusion: Thus we provided a novel therapy strategy for clinical treatment of DIPG.
Keywords: BET inhibitor; DIPG; EZH2 inhibitor; Epigenetics; Tumor therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Puget S, Philippe C, Bax DA, Job B, Varlet P, Junier MP, Andreiuolo F, Carvalho D, Reis R, Guerrini-Rousseau L, et al. Mesenchymal transition and PDGFRA amplification/mutation are key distinct oncogenic events in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e30313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030313. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

