14-3-3ζ loss leads to neonatal lethality by microRNA-126 downregulation-mediated developmental defects in lung vasculature
- PMID: 29118970
- PMCID: PMC5667492
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-017-0186-y
14-3-3ζ loss leads to neonatal lethality by microRNA-126 downregulation-mediated developmental defects in lung vasculature
Abstract
Background: The 14-3-3 family of proteins have been reported to play an important role in development in various mouse models, but the context specific developmental functions of 14-3-3ζ remain to be determined. In this study, we identified a context specific developmental function of 14-3-3ζ.
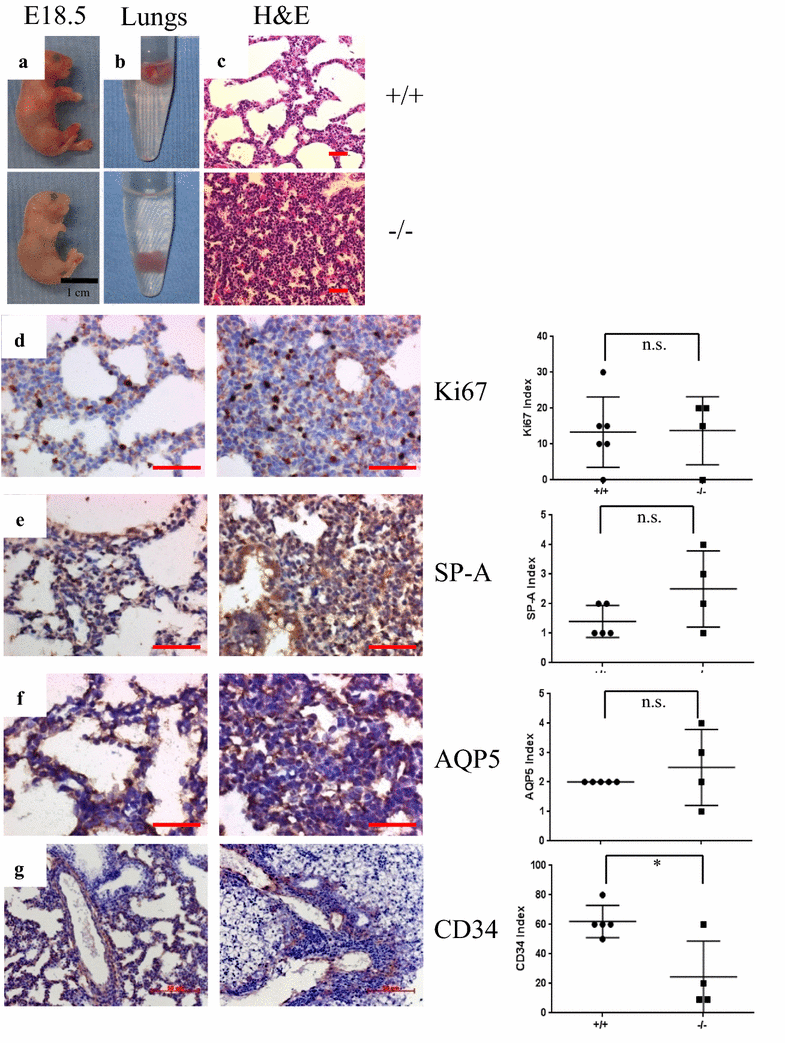
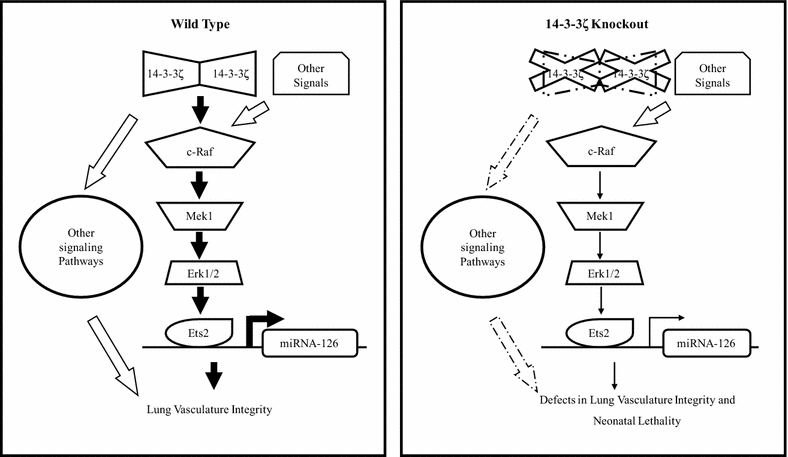
Results: Targeted deletion of 14-3-3ζ in the C57Bl/6J murine genetic background led to neonatal lethality due to respiratory distress and could be rescued by out-breeding to the CD-1 or backcrossing to the FVB/NJ congenic background. Histological analysis of lung sections from 18.5 days post coitum embryos (dpc) showed that 14-3-3ζ-/- lung development is arrested at the pseudoglandular stage and exhibits vascular defects. The expression of miR-126, an endothelial-specific miRNA known to regulate lung vascular integrity was down-regulated in the lungs of the 14-3-3ζ-/- embryos in the C57Bl/6J background as compared to their wild-type counterparts. Loss of 14-3-3ζ in endothelial cells inhibited the angiogenic capability of the endothelial cells as determined by both trans-well migration assays and tube formation assays and these defects could be rescued by re-expressing miR-126. Mechanistically, loss of 14-3-3ζ led to reduced Erk1/2 phosphorylation resulting in attenuated binding of the transcription factor Ets2 on the miR-126 promoter which ultimately reduced expression of miR-126.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrates that miR-126 is an important angiogenesis regulator that functions downstream of 14-3-3ζ and downregulation of miR-126 plays a critical role in 14-3-3ζ-loss induced defects in lung vasculature in the C57Bl/6J genetic background.
Keywords: 14-3-3ζ; Angiogenesis; Lung development; miR-126.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Altered expression of 14-3-3ζ protein in spinal cords of rat fetuses with spina bifida aperta.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 6;8(8):e70457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070457. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936434 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-Based Therapy of GATA2-Deficient Vascular Disease.Circulation. 2016 Dec 13;134(24):1973-1990. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.022478. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 27780851
-
MicroRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta.Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 15;70(6):2339-49. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2777. Epub 2010 Mar 9. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20215506
-
miR-451 protects against erythroid oxidant stress by repressing 14-3-3zeta.Genes Dev. 2010 Aug 1;24(15):1620-33. doi: 10.1101/gad.1942110. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20679398 Free PMC article.
-
miR-125a-5p impairs endothelial cell angiogenesis in aging mice via RTEF-1 downregulation.Aging Cell. 2014 Oct;13(5):926-34. doi: 10.1111/acel.12252. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Aging Cell. 2014. PMID: 25059272 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CircRNA_036186 mediates HNSCC progression by regulating 14-3-3ζ.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 3;14:1498139. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1498139. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39691598 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting a chemo-induced adaptive signaling circuit confers therapeutic vulnerabilities in pancreatic cancer.Cell Discov. 2024 Oct 29;10(1):109. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00720-w. Cell Discov. 2024. PMID: 39468013 Free PMC article.
-
The 2017 Ming K. Jeang award for excellence in Cell & Bioscience.Cell Biosci. 2018 Jul 24;8:44. doi: 10.1186/s13578-018-0241-3. eCollection 2018. Cell Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30062005 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental diversity and unique sensitivity to injury of lung endothelial subtypes during postnatal growth.iScience. 2023 Jan 31;26(3):106097. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106097. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36879800 Free PMC article.
-
The MODY-associated KCNK16 L114P mutation increases islet glucagon secretion and limits insulin secretion resulting in transient neonatal diabetes and glucose dyshomeostasis in adults.Elife. 2024 May 3;12:RP89967. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89967. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38700926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu J, Acharya S, Sahin O, Zhang Q, Saito Y, Yao J, Wang H, Li P, Zhang L, Lowery FJ, et al. 14-3-3zeta turns TGF-beta’s function from tumor suppressor to metastasis promoter in breast cancer by contextual changes of Smad partners from p53 to Gli2. Cancer Cell. 2015;27(2):177–192. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.11.025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jin J, Smith FD, Stark C, Wells CD, Fawcett JP, Kulkarni S, Metalnikov P, O’Donnell P, Taylor P, Taylor L, et al. Proteomic, functional, and domain-based analysis of in vivo 14-3-3 binding proteins involved in cytoskeletal regulation and cellular organization. Curr Biol CB. 2004;14(16):1436–1450. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.07.051. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angrand PO, Segura I, Volkel P, Ghidelli S, Terry R, Brajenovic M, Vintersten K, Klein R, Superti-Furga G, Drewes G, et al. Transgenic mouse proteomics identifies new 14-3-3-associated proteins involved in cytoskeletal rearrangements and cell signaling. Mol Cell Proteom MCP. 2006;5(12):2211–2227. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M600147-MCP200. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

