Effects of Propofol Treatment in Neural Progenitors Derived from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 29119024
- PMCID: PMC5651106
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9182748
Effects of Propofol Treatment in Neural Progenitors Derived from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
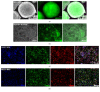
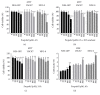
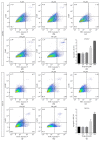
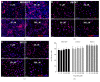
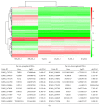
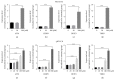
Propofol is an intravenous anesthetic that has been widely used in clinics. Besides its anesthetic effects, propofol has also been reported to influence the regulation of the autonomic system. Controversies exist with regard to whether propofol exposure is safe for pregnant women and young children. In this work, human-induced pluripotent stem cell- (hiPSC-) derived neural progenitor cells (NPCs) were treated with propofol at 20, 50, 100, or 300 μM for 6 h or 24 h, and acute and subacute cell injury, cell proliferation, and apoptosis were evaluated. Comparison of genome-wide gene expression profiles was performed for treated and control iPSC-NPCs. Propofol treatment for 6 h at the clinically relevant concentration (20 or 50 μM) did not affect cell viability, apoptosis, or proliferation, while propofol at higher concentration (100 or 300 μM) decreased NPC viability and induced apoptosis. In addition, 20 μM propofol treatment for 6 h did not alter global gene expression. In summary, propofol treatment at commonly practiced clinical doses for 6 h did not have adverse effects on hiPSC-derived NPCs. In contrast, longer exposure and/or higher concentration could decrease NPC viability and induce apoptosis.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

