Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3651 is a triple sensor-domain protein
- PMID: 29119630
- PMCID: PMC5775179
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3343
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3651 is a triple sensor-domain protein
Abstract
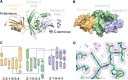
The genome of the human pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) encodes ∼4,400 proteins, but one third of them have unknown functions. We solved the crystal structure of Rv3651, a hypothetical protein with no discernible similarity to proteins with known function. Rv3651 has a three-domain architecture that combines one cGMP-specific phosphodiesterases, adenylyl cyclases and FhlA (GAF) domain and two Per-ARNT-Sim (PAS) domains. GAF and PAS domains are sensor domains that are typically linked to signaling effector molecules. Unlike these sensor-effector proteins, Rv3651 is an unusual sensor domain-only protein with highly divergent sequence. The structure suggests that Rv3651 integrates multiple different signals and serves as a scaffold to facilitate signal transfer.
Keywords: GAF domain; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; PAS domain; proteins of unknown function.
© 2017 The Protein Society.
Figures

References
-
- Baker EN, Arcus VL, Lott JS (2003) Protein structure prediction and analysis as a tool for functional genomics. Appl Bioinform 2:S3–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

