Carbonate apatite nanoparticles carry siRNA(s) targeting growth factor receptor genes egfr1 and erbb2 to regress mouse breast tumor
- PMID: 29119846
- PMCID: PMC8240997
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1396385
Carbonate apatite nanoparticles carry siRNA(s) targeting growth factor receptor genes egfr1 and erbb2 to regress mouse breast tumor
Abstract
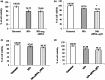
Cancer cells lose their control on cell cycle by numerous genetic and epigenetic alterations. In a tumor, these cells highly express growth factor receptors (GFRs), eliciting growth, and cell division. Among the GFRs, epidermal growth factor receptor-1 (EGFR1) (Her1/ERBB1) and epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (EGFR2) (Her2/ERBB2) from epidermal growth factor (EGF) family and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) are highly expressed on breast cancer cells, thus contributing to the aggressive growth and invasiveness, have been focused in this study. Moreover, overexpression of these receptors is related to suppression of cell death and conferring resistance against the classical drugs used to treat cancer nowadays. Therefore, silencing of these GFRs-encoding genes by using selective small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) could be a powerful approach to treat breast cancer. The inorganic pH sensitive carbonate apatite nanoparticles (NPs) were used as a nano-carrier to deliver siRNA(s) against single or multiple GFR genes in breast cancer cells as well as in a mouse model of breast carcinoma. Silencing of egfr1 and erbb2 simultaneously led to a reduction in cell viability with an increase in cell death signal in the cancer cells and regression of tumor growth in vivo.
Keywords: Growth factor receptors; breast cancer; carbonate apatite nanoparticles (NPs); gene silencing; siRNA; tumor regression.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures



References
-
- Allen LF, Lenehan PF, Eiseman IA, et al. . (2002). Potential benefits of the irreversible pan-erbB inhibitor, CI-1033, in the treatment of breast cancer. Semin Oncol 29:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Butt AJ, Firth SM, Baxter RC. (1999). The IGF axis and programmed cell death. Immunol Cell Biol 77:256–62. - PubMed
-
- Campiglio M, Locatelli A, Olgiati C, et al. . (2004). Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in breast cancer cells by the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (‘Iressa’) is independent of EGFR expression level. J Cell Physiol 198:259–68. - PubMed
-
- Chong YM, Colston K, Jiang WG, et al. . (2006). The relationship between the insulin-like growth factor-1 system and the oestrogen metabolising enzymes in breast cancer tissue and its adjacent non-cancerous tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 99:275–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
