Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Predicts Outcome in Complex Aortic Surgery
- PMID: 29120365
- PMCID: PMC5713343
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18112374
Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Predicts Outcome in Complex Aortic Surgery
Abstract
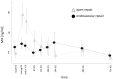
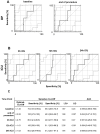
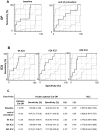
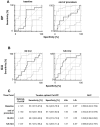
The perioperative inflammatory response is associated with outcome after complex aortic repair. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) shows protective effects in ischemia-reperfusion (IR), but also adverse pro-inflammatory effects in acute inflammation, potentially leading to adverse outcome, which should be investigated in this trial. This prospective study enrolled 52 patients, of whom 29 (55.7%) underwent open repair (OR) and 23 (44.3%) underwent endovascular repair (ER) between 2014 and 2015. MIF serum levels were measured until 72 h post-operatively. We used linear mixed models and ROC analysis to analyze the MIF time-course and its diagnostic ability. Compared to ER, OR induced higher MIF release perioperatively; at 12 h after ICU admission, MIF levels were similar between groups. MIF course was significantly influenced by baseline MIF level (P = 0.0016) and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) II score (P = 0.0005). MIF level at 24 h after ICU admission showed good diagnostic value regarding patient survival [sensitivity, 80.0% (28.4-99.5%); specificity, 51.2% (35.1-67.1%); AUC, 0.688 (0.534-0.816)] and discharge modality [sensitivity, 87.5% (47.3-99.7%); specificity, 73.7% (56.9-86.6%), AUC, 0.789 (0.644-0.896)]. Increased perioperative MIF-levels are related to an increased risk of adverse outcome in complex aortic surgery and may represent a biomarker for risk stratification in complex aortic surgery.
Keywords: intensive care unit; macrophage migration inhibitory factor; survival; thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Payen D., Lukaszewicz A.C., Legrand M., Gayat E., Faivre V., Megarbane B., Azoulay E., Fieux F., Charron D., Loiseau P., et al. A multicentre study of acute kidney injury in severe sepsis and septic shock: Association with inflammatory phenotype and HLA genotype. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e35838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035838. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Abed Y., Dabideen D., Aljabari B., Valster A., Messmer D., Ochani M., Tanovic M., Ochani K., Bacher M., Nicoletti F., et al. ISO-1 binding to the tautomerase active site of MIF inhibits its pro-inflammatory activity and increases survival in severe sepsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:36541–36544. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500243200. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

