Staphylococcus aureus Epicutaneous Exposure Drives Skin Inflammation via IL-36-Mediated T Cell Responses
- PMID: 29120743
- PMCID: PMC5774218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.10.006
Staphylococcus aureus Epicutaneous Exposure Drives Skin Inflammation via IL-36-Mediated T Cell Responses
Abstract
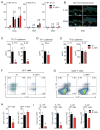
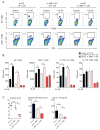
Staphylococcus aureus colonization contributes to skin inflammation in diseases such as atopic dermatitis, but the signaling pathways involved are unclear. Herein, epicutaneous S. aureus exposure to mouse skin promoted MyD88-dependent skin inflammation initiated by IL-36, but not IL-1α/β, IL-18, or IL-33. By contrast, an intradermal S. aureus challenge promoted MyD88-dependent host defense initiated by IL-1β rather than IL-36, suggesting that different IL-1 cytokines trigger MyD88 signaling depending on the anatomical depth of S. aureus cutaneous exposure. The bacterial virulence factor PSMα, but not α-toxin or δ-toxin, contributed to the skin inflammation, which was driven by IL-17-producing γδ and CD4+ T cells via direct IL-36R signaling in the T cells. Finally, adoptive transfer of IL-36R-expressing T cells to IL-36R-deficient mice was sufficient for mediating S. aureus-induced skin inflammation. Together, this study defines a previously unknown pathway by which S. aureus epicutaneous exposure promotes skin inflammation involving IL-36R/MyD88-dependent IL-17 T cell responses.
Keywords: IL-17; IL-36; Staphylococcus aureus; T cell; atopic dermatitis; cutaneous; epicutaneous; inflammation; phenol soluble modulin; skin.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Staphylococcus aureus: Master Manipulator of the Skin.Cell Host Microbe. 2017 Nov 8;22(5):579-581. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.10.015. Cell Host Microbe. 2017. PMID: 29120738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breuer K, SHA, Kapp A, Werfel T. Staphylococcus aureus: colonizing features and influence of an antibacterial treatment in adults with atopic dermatitis. The British journal of dermatology. 2002;147:55–61. - PubMed
-
- Carrier Y, Ma HL, Ramon HE, Napierata L, Small C, O’Toole M, Young DA, Fouser LA, Nickerson-Nutter C, Collins M, et al. Inter-regulation of Th17 cytokines and the IL-36 cytokines in vitro and in vivo: implications in psoriasis pathogenesis. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 2011;131:2428–2437. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

