Effects of decades of physical driving on body movement and motion sickness during virtual driving
- PMID: 29121059
- PMCID: PMC5679615
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187120
Effects of decades of physical driving on body movement and motion sickness during virtual driving
Abstract
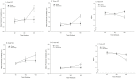
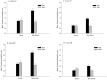
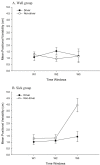
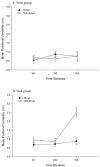
We investigated relations between experience driving physical automobiles and motion sickness during the driving of virtual automobiles. Middle-aged individuals drove a virtual automobile in a driving video game. Drivers were individuals who had possessed a driver's license for approximately 30 years, and who drove regularly, while non-drivers were individuals who had never held a driver's license, or who had not driven for more than 15 years. During virtual driving, we monitored movement of the head and torso. During virtual driving, drivers became motion sick more rapidly than non-drivers, but the incidence and severity of motion sickness did not differ as a function of driving experience. Patterns of movement during virtual driving differed as a function of driving experience. Separately, movement differed between participants who later became motion sick and those who did not. Most importantly, physical driving experience influenced patterns of postural activity that preceded motion sickness during virtual driving. The results are consistent with the postural instability theory of motion sickness, and help to illuminate relations between the control of physical and virtual vehicles.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of physical driving experience on body movement and motion sickness among passengers in a virtual vehicle.Exp Brain Res. 2021 Feb;239(2):491-500. doi: 10.1007/s00221-020-05940-6. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Exp Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33242143
-
Effects of Physical Driving Experience on Body Movement and Motion Sickness During Virtual Driving.Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2017 Nov 1;88(11):985-992. doi: 10.3357/AMHP.4893.2017. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2017. PMID: 29046173
-
Control of a virtual vehicle influences postural activity and motion sickness.J Exp Psychol Appl. 2011 Jun;17(2):128-38. doi: 10.1037/a0024097. J Exp Psychol Appl. 2011. PMID: 21604911
-
Self-driving carsickness.Appl Ergon. 2016 Mar;53 Pt B:374-82. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2015.09.009. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Appl Ergon. 2016. PMID: 26446454 Review.
-
Visual Vertigo, Motion Sickness, and Disorientation in Vehicles.Semin Neurol. 2020 Feb;40(1):116-129. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1701653. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Semin Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32045940 Review.
Cited by
-
Hazard Perception, Presence, and Simulation Sickness-A Comparison of Desktop and Head-Mounted Display for Driving Simulation.Front Psychol. 2021 Apr 22;12:647723. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.647723. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33967907 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Affecting Car Sickness of Passengers Traveled by Vehicles in North Shewa Zone, Oromia, Ethiopia.J Environ Public Health. 2022 Feb 22;2022:6642603. doi: 10.1155/2022/6642603. eCollection 2022. J Environ Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35242196 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual reality technology in the rehabilitation of post-stroke cognitive impairment: an opinion article on recent findings.Front Psychol. 2023 Oct 2;14:1271458. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1271458. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37849482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of physical driving experience on body movement and motion sickness among passengers in a virtual vehicle.Exp Brain Res. 2021 Feb;239(2):491-500. doi: 10.1007/s00221-020-05940-6. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Exp Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33242143
-
Postural time-to-contact as a precursor of visually induced motion sickness.Exp Brain Res. 2018 Jun;236(6):1631-1641. doi: 10.1007/s00221-018-5246-y. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Exp Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29589080
References
-
- Stevens S. C., & Parsons M. G. (2002). Effects of motion at sea on crew performance: A survey. Marine Tech 39:29–47.
-
- Murphy-Hill E., Zimmerman T., & Nagappan N. (2014). Cowboys, ankle sprains, and keepers of quality: How is video game development different from software development? Proc 36th Int Conf Software Eng:1–11. doi: 10.1145/2568225.2568226 - DOI
-
- Oman C. M. (1982). A heuristic mathematical model for the dynamics of sensory conflict and motion sickness. Acta Oto-Laryngol Suppl 392:44. - PubMed
-
- Young L. R. (1984). Perception of the body in space: Mechanisms In Smith I. (Ed.), Handbook of Physiology—The Nervous System (Vol. 3, pp. 1023–1066). New York: Academic Press.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

