Fission yeast strains with circular chromosomes require the 9-1-1 checkpoint complex for the viability in response to the anti-cancer drug 5-fluorodeoxyuridine
- PMID: 29121084
- PMCID: PMC5679574
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187775
Fission yeast strains with circular chromosomes require the 9-1-1 checkpoint complex for the viability in response to the anti-cancer drug 5-fluorodeoxyuridine
Abstract
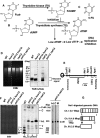
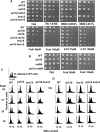
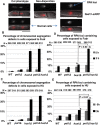
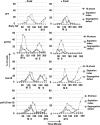
Thymidine kinase converts 5-fluorodeoxyuridine to 5-fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate, which causes disruption of deoxynucleotide triphosphate ratios. The fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe does not express endogenous thymidine kinase but 5-fluorodeoxyuridine inhibits growth when exogenous thymidine kinase is expressed. Unexpectedly, we found that 5-fluorodeoxyuridine causes S phase arrest even without thymidine kinase expression. DNA damage checkpoint proteins such as the 9-1-1 complex were required for viability in the presence of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine. We also found that strains with circular chromosomes, due to loss of pot1+, which have higher levels of replication stress, were more sensitive to loss of the 9-1-1 complex in the presence of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine. Thus, our results suggest that strains carrying circular chromosomes exhibit a greater dependence on DNA damage checkpoints to ensure viability in the presence of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine compared to stains that have linear chromosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sakamoto K, Yokogawa T, Ueno H, Oguchi K, Kazuno H, Ishida K, et al. Crucial roles of thymidine kinase 1 and deoxyUTPase in incorporating the antineoplastic nucleosides trifluridineand 2'-deoxy-5-fluorouridine into DNA. Int J Oncol. 2015;46: 2327–2334. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.2974 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wilson PM, Danenberg PV, Johnston PG, Lenz HJ, Ladner RD. Standing the test of time: targeting thymidylate biosynthesis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014;11: 282–298. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.51 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Longley DB, Harkin DP, Johnston PG. 5-fluorouracil: mechanisms of Action and clinical strategies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3: 330–338. doi: 10.1038/nrc1074 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huehls AM, Wagner JM, Huntoon CJ, Geng L, Erlichman C, Patel AG, et al. Poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerase inhibition synergizes with 5-fluorodeoxyuridine but not 5-fluorouracil in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2011;71: 4944–4954. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0814 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Delacroix S, Wagner JM, Kobayashi M, Yamamoto K, Karnitz LM. The Rad9-Hus1-Rad1 (9-1-1) clamp activates checkpoint signaling via TopBP1. Genes Dev. 2007;21: 1472–1477. doi: 10.1101/gad.1547007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

