Diagnostic Value of Serum-Soluble Interleukin 2 Receptor Levels vs Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Patients With Sarcoidosis-Associated Uveitis
- PMID: 29121154
- PMCID: PMC6583850
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.4771
Diagnostic Value of Serum-Soluble Interleukin 2 Receptor Levels vs Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Patients With Sarcoidosis-Associated Uveitis
Abstract
Importance: New and improved diagnostic tests for sarcoidosis-associated uveitis are needed because the currently available laboratory diagnostic biomarkers (eg, lysozyme and angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE]) are lacking in high sensitivity and specificity.
Objective: To compare the value of soluble interleukin 2 receptor (sIL-2R) with ACE as diagnostic biomarkers of sarcoidosis in patients with uveitis.
Design, setting, and participants: A cross-sectional retrospective study was conducted using data collected from 249 consecutive patients with uveitis at the Erasmus University Medical Center uveitis outpatient clinic, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, from April 3, 2013, through November 25, 2015. Measurements of sIL-2R and ACE in serum samples and data extraction from patient files were conducted from December 2016 through February 2017, and analysis from April to May 2017.
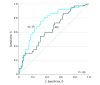
Main outcomes and measures: Serum levels of sIL-2R and ACE and chest radiographic findings were assessed. Receiver operating characteristics analysis was used to determine the probability that individual tests correctly identified patients with sarcoidosis. The Youden Index was used to determine the optimal cutoff points for serum sIL-2R and ACE levels to define sarcoidosis in patients with uveitis.
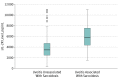
Results: Data were analyzed from 249 patients with uveitis who had their serum sIL-2R and ACE levels determined and underwent chest radiography. Mean (SD) age at the time of sampling was 51 (16) years, 161 patients (64.7%) were women, and 191 (76.7%) were white. Although patients with sarcoidosis-associated uveitis had the highest mean (SD) serum sIL-2R (6047 [2533] pg/mL) and ACE (61 [38] U/L) levels, elevated serum sIL-2R levels were also found in patients with HLA-B27–associated (4460 [2465] pg/mL) and varicella-zoster virus–associated (5386 [1778] pg/mL) uveitis. Serum sIL-2R and ACE levels were significantly correlated (Pearson correlation coefficient, 0.205; P = .001, 2-sided), but no association was found between uveitis activity and sIL-2R (Spearman rank correlation coefficient [ρ], 0.070, P = .27) nor uveitis activity and ACE (ρ, −0.071; P = .27). The highest Youden index for sIL-2R alone was 0.45, corresponding to an optimal cutoff of 4000 pg/mL and providing 81% (95% CI, 74%-89%) sensitivity and 64% (95% CI, 56%-72%) specificity alone but combined with chest radiography yielded 92% sensitivity and 58% specificity. Chest radiography combined with sIL-2R at a cutoff of 6000 pg/mL resulted in 77% sensitivity and 73% specificity. Combined chest radiography and serum ACE levels at the standard cutoff of 68 U/L resulted in 70% sensitivity and 79% specificity.
Conclusions and relevance: This cross-sectional study demonstrates that sIL-2R is a useful marker for diagnosing sarcoidosis in patients with uveitis and has slightly better diagnostic value than ACE.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Sarcoid, Bayes, and the Challenges of Laboratory Testing for Uveitis.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017 Dec 1;135(12):1359-1360. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.4789. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29121149 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor level is more sensitive than angiotensin-converting enzyme or lysozyme for diagnosis of sarcoidosis and may be a marker of multiple organ involvement.J Dermatol. 2017 Jul;44(7):789-797. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.13792. Epub 2017 Mar 11. J Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28295528
-
Sensitivity and specificity of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor for diagnosing sarcoidosis in a population of patients suspected of sarcoidosis.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 17;14(10):e0223897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223897. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31622413 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-2 Receptor and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme as Markers for Ocular Sarcoidosis.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 22;11(1):e0147258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147258. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26799486 Free PMC article.
-
Value of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in sarcoidosis.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020 Jul;14(7):749-756. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2020.1751614. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32248706 Review.
-
Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Sarcoidosis: Current Use and Future Prospects.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1443. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01443. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32760396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A serum B-lymphocyte activation signature is a key distinguishing feature of the immune response in sarcoidosis compared to tuberculosis.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 10;7(1):1114. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06822-1. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39256610 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcoidosis-Related Uveitis: A Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 29;12(9):3194. doi: 10.3390/jcm12093194. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37176633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Findings and Graduation of Sarcoidosis-Related Uveitis: A Single-Center Study.Cells. 2021 Dec 29;11(1):89. doi: 10.3390/cells11010089. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011651 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Metabolomic Profiling of Patients with Non-Infectious Uveitis.J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 6;9(12):3955. doi: 10.3390/jcm9123955. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33291298 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Serum Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Diagnosing Sarcoidosis and Predicting the Active Status of Sarcoidosis: A Meta-Analysis.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 30;12(10):1400. doi: 10.3390/biom12101400. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsirouki T, Dastiridou A, Symeonidis C, et al. . A focus on the epidemiology of uveitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2016:1-15. - PubMed
-
- Herbort CP, Rao NA, Mochizuki M; members of Scientific Committee of First International Workshop on Ocular Sarcoidosis . International criteria for the diagnosis of ocular sarcoidosis: results of the first International Workshop on Ocular Sarcoidosis (IWOS). Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2009;17(3):160-169. - PubMed
-
- Baughman RP, Lower EE, Kaufman AH. Ocular sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):452-462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

