P-glycoproteins play a role in ivermectin resistance in cyathostomins
- PMID: 29121562
- PMCID: PMC5681340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2017.10.006
P-glycoproteins play a role in ivermectin resistance in cyathostomins
Abstract
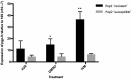
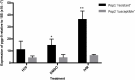
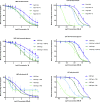
Anthelmintic resistance is a global problem that threatens sustainable control of the equine gastrointestinal cyathostomins (Phylum Nematoda; Superfamily Strongyloidea). Of the three novel anthelmintic classes that have reached the veterinary market in the last decade, none are currently licenced in horses, hence current control regimens focus on prolonging the useful lifespan of licenced anthelmintics. This approach would be facilitated by knowledge of the resistance mechanisms to the most widely used anthelmintics, the macrocyclic lactones (ML). There are no data regarding resistance mechanisms to MLs in cyathostomins, although in other parasitic nematodes, the ABC transporters, P-glycoproteins (P-gps), have been implicated in playing an important role. Here, we tested the hypothesis that P-gps are, at least in part, responsible for reduced sensitivity to the ML ivermectin (IVM) in cyathostomins; first, by measuring transcript levels of pgp-9 in IVM resistant versus IVM sensitive third stage larvae (L3) pre-and post-IVM exposure in vitro. We then tested the effect of a range of P-gp inhibitors on the effect of IVM against the same populations of L3 using the in vitro larval development test (LDT) and larval migration inhibition test (LMIT). We demonstrated that, not only was pgp-9 transcription significantly increased in IVM resistant compared to IVM sensitive L3 after anthelmintic exposure (p < 0.001), but inhibition of P-gp activity significantly increased sensitivity of the larvae to IVM in vitro, an effect only observed in the IVM resistant larvae in the LMIT. These data strongly implicate a role for P-gps in IVM resistance in cyathostomins. Importantly, this raises the possibility that P-gp inhibitor-IVM combination treatments might be used in vivo to increase the effectiveness of IVM against cyathostomins in Equidae.
Keywords: Anthelmintic resistance; Cyathostomins; Ivermectin; P-glycoproteins.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative DNA metabarcoding reveals species composition of a macrocyclic lactone and pyrantel resistant cyathostomin population in the UK.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2025 Apr;27:100576. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2024.100576. Epub 2024 Dec 22. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39778419 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the larval migration inhibition test for comparative analysis of ivermectin sensitivity in cyathostomin populations.Vet Parasitol. 2015 Sep 15;212(3-4):292-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.06.019. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Vet Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26120037
-
Effects of in vitro exposure to ivermectin and levamisole on the expression patterns of ABC transporters in Haemonchus contortus larvae.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2016 Aug;6(2):103-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2016. PMID: 27164439 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to avermectin/milbemycin anthelmintics in equine cyathostomins - current situation.Vet Parasitol. 2012 Apr 19;185(1):16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.10.013. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Vet Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22047763 Review.
-
The in vitro diagnosis of anthelmintic resistance in cyathostomins.Vet Parasitol. 2012 Apr 19;185(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.10.014. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Vet Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22100398 Review.
Cited by
-
Caenorhabditis elegans in anthelmintic research - Old model, new perspectives.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2020 Dec;14:237-248. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33249235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sub-lethal doses of albendazole induce drug metabolizing enzymes and increase albendazole deactivation in Haemonchus contortus adults.Vet Res. 2020 Jul 23;51(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00820-x. Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32703268 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative DNA metabarcoding reveals species composition of a macrocyclic lactone and pyrantel resistant cyathostomin population in the UK.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2025 Apr;27:100576. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2024.100576. Epub 2024 Dec 22. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39778419 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effect of Berberine on Broiler P-glycoprotein Expression and Function: In Situ and In Vitro Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 22;20(8):1966. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081966. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31013627 Free PMC article.
-
Differential ABC transporter gene expression in adult Dirofilaria immitis males and females following in vitro treatment with ivermectin, doxycycline or a combination of both.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Aug 13;12(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3645-y. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31409391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AlGusbi S., Krucken J., Ramunke S., von Samson-Himmelstjerna G., Demeler J. Analysis of putative inhibitors of anthelmintic resistance mechanisms in cattle gastrointestinal nematodes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014;44:647–658. - PubMed
-
- Ardelli B.F. Transport proteins of the ABC systems superfamily and their role in drug action and resistance in nematodes. Parasitol. Int. 2013;62:639–646. - PubMed
-
- Ardelli B.F., Guerriero S.B., Prichard R.K. Genomic organization and effects of ivermectin selection on Onchocerca volvulus P-glycoprotein. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2005;143:58–66. - PubMed
-
- Ardelli B.F., Prichard R.K. Reduced genetic variation of an Onchocerca volvulus ABC transporter gene following treatment with ivermectin. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007;101:1223–1232. - PubMed
-
- Ardelli B.F., Prichard R.K. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein enhances sensitivity of Caenorhabditis elegans to ivermectin. Vet. Parasitol. 2013;191:264–275. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

