Ethical aspects of brain computer interfaces: a scoping review
- PMID: 29121942
- PMCID: PMC5680604
- DOI: 10.1186/s12910-017-0220-y
Ethical aspects of brain computer interfaces: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is a set of technologies that are of increasing interest to researchers. BCI has been proposed as assistive technology for individuals who are non-communicative or paralyzed, such as those with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or spinal cord injury. The technology has also been suggested for enhancement and entertainment uses, and there are companies currently marketing BCI devices for those purposes (e.g., gaming) as well as health-related purposes (e.g., communication). The unprecedented direct connection created by BCI between human brains and computer hardware raises various ethical, social, and legal challenges that merit further examination and discussion.
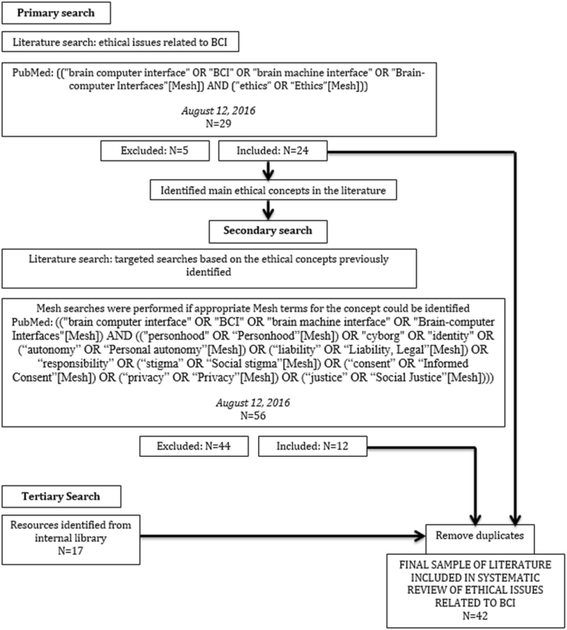
Methods: To identify and characterize the key issues associated with BCI use, we performed a scoping review of biomedical ethics literature, analyzing the ethics concerns cited across multiple disciplines, including philosophy and medicine.
Results: Based on this investigation, we report that BCI research and its potential translation to therapeutic intervention generate significant ethical, legal, and social concerns, notably with regards to personhood, stigma, autonomy, privacy, research ethics, safety, responsibility, and justice. Our review of the literature determined, furthermore, that while these issues have been enumerated extensively, few concrete recommendations have been expressed.
Conclusions: We conclude that future research should focus on remedying a lack of practical solutions to the ethical challenges of BCI, alongside the collection of empirical data on the perspectives of the public, BCI users, and BCI researchers.
Keywords: Brain-computer interface; Brain-machine interface; Ethics of technology; Scoping review.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Similar articles
-
Using brain-computer interfaces: a scoping review of studies employing social research methods.BMC Med Ethics. 2019 Mar 7;20(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12910-019-0354-1. BMC Med Ethics. 2019. PMID: 30845952 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Suggestions of Ethical Review on Clinical Research Involving Brain-Computer Interfaces.Chin Med Sci J. 2024 Jun 30;39(2):131-139. doi: 10.24920/004377. Chin Med Sci J. 2024. PMID: 38862406
-
Ethical issues in brain-computer interface research, development, and dissemination.J Neurol Phys Ther. 2012 Jun;36(2):94-9. doi: 10.1097/NPT.0b013e31825064cc. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2012. PMID: 22592066
-
Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control.Clin Neurophysiol. 2002 Jun;113(6):767-91. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(02)00057-3. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 12048038 Review.
-
Identifying Thematics in a Brain-Computer Interface Research.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Jan 4;2023:2793211. doi: 10.1155/2023/2793211. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36643889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cochlear implant-specific risks should be considered, when assessing the quality of life of children and adolescents with hearing loss and cochlear implants-not just cochlear implant-specific benefits-Perspective.Front Neurosci. 2022 Nov 8;16:985230. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.985230. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36425475 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-computer interfaces, disability, and the stigma of refusal: A factorial vignette study.Public Underst Sci. 2023 May;32(4):522-542. doi: 10.1177/09636625221141663. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Public Underst Sci. 2023. PMID: 36633302 Free PMC article.
-
Public Perception of the Brain-Computer Interface Based on a Decade of Data on X: Mixed Methods Study.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Jun 25;9:e60859. doi: 10.2196/60859. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 40561510 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of brain-computer interfaces and artificial intelligence: applications and challenges.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Jun;8(11):712. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.11.109. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32617332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Ethical considerations for medical applications of implantable brain-computer interfaces].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 25;41(1):177-183. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202309083. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38403619 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Clausen J. Conceptual and ethical issues with brain-hardware interfaces. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2011;24(6):495–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources