Sinonasal T-cell expression of cytotoxic mediators granzyme B and perforin is reduced in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 29122079
- PMCID: PMC5691237
- DOI: 10.2500/ajra.2017.31.4474
Sinonasal T-cell expression of cytotoxic mediators granzyme B and perforin is reduced in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
Abstract
Background: CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells are cytotoxic cells that use granzyme B (GrB) and perforin. Defective cytotoxic function is known to play a role in dysregulated immune response as seen in chronic sinusitis, also referred to as chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). However, to our knowledge, in the United States, neither GrB or perforin expression has been reported in patients with CRS.
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate sinonasal cytotoxic cells, their mediators, and cell-specific distribution of these mediators in patients with CRS with nasal polyp (CRSwNP) and in patients with CRS without nasal polyp (CRSsNP).
Methods: Blood and sinus tissue samples were taken from patients with CRSsNP (n = 8) and CRSwNP (n = 8) at the time of surgery. Control subjects (n = 8) underwent surgery for cerebrospinal fluid leak repair or to remove non-hormone-secreting pituitary tumors. The cells were analyzed via flow cytometry by using CD8 expression to identify cytotoxic T cells and CD56 expression to identify NK cells. Intracellular GrB and perforin expression were analyzed with flow cytometry.
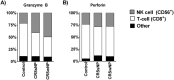
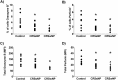
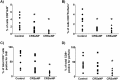
Results: We observed no significant differences in plasma or peripheral blood immune cell numbers or specific levels of GrB or perforin among the groups. In the sinonasal mucosa of the patients with CRSsNP and the patients with CRSwNP, there was a significant decrease in GrB and perforin levels (p < 0.05) despite similar or increased numbers of cytotoxic cells when compared with the controls. The overall decrease in GrB and perforin in the sinonasal mucosa of the patients with CRSsNP and the patients with CRSwNP was due to decreased T cell production. There was no difference in total NK cell count or expression of perforin or GrB among all the groups.
Conclusion: Total levels of sinonasal GrB and perforin were decreased in the sinonasal mucosa of both the patients with CRSwNP and the patients with CRSsNP compared with the controls, whereas sinonasal CD8+ T cells, (but not NK cells,), intracellular stores of GrB and perforin were reduced in the patients with CRSwNP compared with the controls.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare pertaining to this article
Figures


Similar articles
-
IL-17A-producing sinonasal MAIT cells in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Feb;149(2):599-609.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.07.037. Epub 2021 Aug 14. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34403659
-
Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009 Sep;124(3):478-84, 484.e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.017. Epub 2009 Jul 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19541359
-
Reduced sinonasal levels of 1α-hydroxylase are associated with worse quality of life in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016 Jan;6(1):58-65. doi: 10.1002/alr.21576. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016. PMID: 26575398
-
T regulatory and Th17 cells in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016 Aug;6(8):826-34. doi: 10.1002/alr.21742. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016. PMID: 27012842
-
New insights into upper airway innate immunity.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016 Sep;30(5):319-23. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4360. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016. PMID: 27657896 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endotyping in Chronic Rhinosinusitis-An EAACI Task Force Report.Allergy. 2025 Jan;80(1):132-147. doi: 10.1111/all.16418. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Allergy. 2025. PMID: 39641584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological Aspects of Chronic Rhinosinusitis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;12(10):2361. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102361. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel Granzyme B nanoparticle delivery system simulates immune cell functions for suppression of solid tumors.Theranostics. 2019 Oct 14;9(25):7616-7627. doi: 10.7150/thno.35900. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31695790 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone Alters Tracheal Aspirate T-Cell Cytokine Production in Ventilated Preterm Infants.Children (Basel). 2021 Oct 2;8(10):879. doi: 10.3390/children8100879. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34682144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel ZM, Thamboo A, Rudmik L, et al. Surgical therapy vs continued medical therapy for medically refractory chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 7:119–127, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Voskoboinik I, Whisstock JC, Trapani JA. Perforin and granzymes: Function, dysfunction and human pathology. Nat Rev Immunol 15:388–400, 2015. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

