Aurora A Functional Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Correlates With Clinical Outcome in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors Treated With Alisertib, an Investigational Aurora A Kinase Inhibitor
- PMID: 29122619
- PMCID: PMC5704062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.10.015
Aurora A Functional Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Correlates With Clinical Outcome in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors Treated With Alisertib, an Investigational Aurora A Kinase Inhibitor
Abstract
Background: Alisertib (MLN8237) is an investigational, oral, selective Aurora A kinase inhibitor. Aurora A contains two functional single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs; codon 31 [F/I] and codon 57 [V/I]) that lead to functional changes. This study investigated the prognostic and predictive significance of these SNPs.
Methods: This study evaluated associations between Aurora A SNPs and overall survival (OS) in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The Aurora A SNPs were also evaluated as predictive biomarkers for clinical outcomes to alisertib in two phase 2 studies (NCT01045421 and NCT01091428). Aurora A SNP genotyping was obtained from 85 patients with advanced solid tumors receiving single-agent alisertib and 122 patients with advanced recurrent ovarian cancer treated with alisertib plus weekly paclitaxel (n=62) or paclitaxel alone (n=60). Whole blood was collected prior to treatment and genotypes were analyzed by PCR.
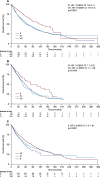
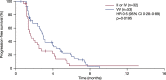
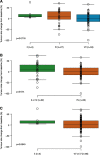
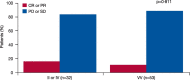
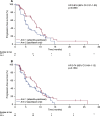
Findings: TCGA data suggested prognostic significance for codon 57 SNP; solid tumor patients with VV and VI alleles had significantly reduced OS versus those with II alleles (HR 1.9 [VI] and 1.8 [VV]; p<0.0001). In NCT01045421, patients carrying the VV alleles at codon 57 (n=53, 62%) had significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) than patients carrying IV or II alleles (n=32, 38%; HR 0.5; p=0.0195). In NCT01091428, patients with the VV alleles at codon 57 who received alisertib plus paclitaxel (n=47, 39%) had a trend towards improved PFS (7.5months) vs paclitaxel alone (n=32, 26%; 3.8months; HR 0.618; p=0.0593). In the paclitaxel alone arm, patients with the VV alleles had reduced PFS vs modified intent-to-treat (mITT) patients (3.8 vs 5.1months), consistent with the TCGA study identifying the VV alleles as a poor prognostic biomarker. No significant associations were identified for codon 31 SNP from the same data set.
Interpretation: These findings suggest that Aurora A SNP at codon 57 may predict disease outcome and response to alisertib in patients with solid tumors. Further investigation is warranted.
Keywords: Alisertib; Aurora A kinase inhibitor; Correlative analysis; Predictive biomarker; Prognosis; SNP.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Solid Cancer Treatment With Aurora Kinase Inhibitors: Towards a Personalized Medicine.EBioMedicine. 2017 Nov;25:18-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.10.026. Epub 2017 Oct 31. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 29104076 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Alisertib in Combination With Weekly Paclitaxel in Patients With Advanced Breast Cancer or Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jan 1;5(1):e183773. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3773. Epub 2019 Jan 10. JAMA Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30347019 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Relative bioavailability of a prototype oral solution of the Aurora A kinase inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) in patients with advanced solid tumors.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Jul;53(7):563-72. doi: 10.5414/CP202359. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26073352 Clinical Trial.
-
Association of an aurora kinase a (AURKA) gene polymorphism with progression-free survival in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma treated with the selective aurora kinase a inhibitor alisertib.Invest New Drugs. 2017 Aug;35(4):524-528. doi: 10.1007/s10637-017-0440-5. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Invest New Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28155045
-
Alisertib: a review of pharmacokinetics, efficacy and toxicity in patients with hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Jan;27(1):105-112. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1417382. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29260599 Review.
-
An update on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of alisertib, a selective Aurora kinase A inhibitor.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Jun;43(6):585-601. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12571. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26999067 Review.
Cited by
-
Alisertib in Combination With Weekly Paclitaxel in Patients With Advanced Breast Cancer or Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jan 1;5(1):e183773. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3773. Epub 2019 Jan 10. JAMA Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30347019 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
AURKA rs8173 G>C Polymorphism Decreases Wilms Tumor Risk in Chinese Children.J Oncol. 2019 Sep 15;2019:9074908. doi: 10.1155/2019/9074908. eCollection 2019. J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31636670 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Aurora Kinase A Polymorphism and Epithelial Growth Factor Receptor Mutations on the Clinicopathological Characteristics of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Oct 8;17(19):7350. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17197350. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33050100 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Mesenchymal Markers in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 4;52(1):673. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10745-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40613936 Review.
-
The role of Aurora-A in human cancers and future therapeutics.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 1;10(9):2705-2729. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33042612 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barr A.R., Gergely F. Aurora-A: the maker and breaker of spindle poles. J. Cell Sci. 2007;120(Pt. 17):2987–2996. - PubMed
-
- Cervantes A., Elez E., Roda D. Phase I pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study of MLN8237, an investigational, oral, selective aurora a kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18(17):4764–4774. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

