Limited role of kininogen in the host response during gram-negative pneumonia-derived sepsis
- PMID: 29122754
- PMCID: PMC6842874
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00288.2017
Limited role of kininogen in the host response during gram-negative pneumonia-derived sepsis
Abstract
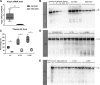
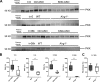
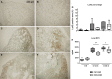
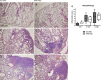
High-molecular-weight kininogen (HK), together with factor XI, factor XII and prekallikrein, is part of the contact system that has proinflammatory, prothrombotic, and vasoactive properties. We hypothesized that HK plays a role in the host response during pneumonia-derived sepsis. To this end mice were depleted of kininogen (KNG) to plasma HK levels of 28% of normal by repeated treatment with a specific antisense oligonucleotide (KNG ASO) for 3 wk before infection with the common human sepsis pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae via the airways. Whereas plasma HK levels increased during infection in mice treated with a scrambled control ASO (Ctrl ASO), HK level in the KNG ASO-treated group remained reduced to 25-30% of that in the corresponding Ctrl ASO group both before and after infection. KNG depletion did not influence bacterial growth in lungs or dissemination to distant body sites. KNG depletion was associated with lower lung CXC chemokine and myeloperoxidase levels but did not impact neutrophil influx, lung pathology, activation of the vascular endothelium, activation of the coagulation system, or the extent of distant organ injury. These results were corroborated by studies in mice with a genetic deficiency of KNG, which were indistinguishable from wild-type mice during Klebsiella-induced sepsis. Both KNG depletion and KNG deficiency were associated with strongly reduced plasma prekallikrein levels, indicating the carrier function of HK for this zymogen. This study suggests that KNG does not significantly contribute to the host defense during gram-negative pneumonia-derived sepsis.
Keywords: contact system; high-molecular weight kininogen; kallikrein-kinin system.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Crosby and A. S. Revenko are employees of Ionis Pharmaceuticals..
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coagulation factor XI improves host defence during murine pneumonia-derived sepsis independent of factor XII activation.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jul 26;117(8):1601-1614. doi: 10.1160/TH16-12-0920. Epub 2017 May 11. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28492700
-
Prekallikrein inhibits innate immune signaling in the lung and impairs host defense during pneumosepsis in mice.J Pathol. 2020 Jan;250(1):95-106. doi: 10.1002/path.5354. Epub 2019 Nov 25. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31595971 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombocytopenia impairs host defense in gram-negative pneumonia-derived sepsis in mice.Blood. 2014 Dec 11;124(25):3781-90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-573915. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25301709 Free PMC article.
-
The plasma contact system as a modulator of innate immunity.Curr Opin Hematol. 2018 Sep;25(5):389-394. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000448. Curr Opin Hematol. 2018. PMID: 30028742 Review.
-
Pathogenic mechanisms of bradykinin mediated diseases: dysregulation of an innate inflammatory pathway.Adv Immunol. 2014;121:41-89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800100-4.00002-7. Adv Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24388213 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiological dynamics in the contact, coagulation, and complement systems during sepsis: Potential targets for nafamostat mesilate.J Intensive Med. 2024 Apr 10;4(4):453-467. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2024.02.003. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Intensive Med. 2024. PMID: 39310056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kininogen supports inflammation and bacterial spreading during Streptococccus Pyogenes Sepsis.EBioMedicine. 2020 Aug;58:102908. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102908. Epub 2020 Jul 21. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32707450 Free PMC article.
-
Kinins and Their Receptors in Infectious Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Aug 27;13(9):215. doi: 10.3390/ph13090215. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32867272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future of sepsis research: time to think differently?Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Sep 1;319(3):L523-L526. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00368.2020. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32755382 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Dynamic Variation of Pulmonary ACE2 Is Required to Modulate Neutrophilic Inflammation in Response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection in Mice.J Immunol. 2019 Dec 1;203(11):3000-3012. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900579. Epub 2019 Oct 23. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31645418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achouiti A, Vogl T, Urban CF, Röhm M, Hommes TJ, van Zoelen MA, Florquin S, Roth J, van ’t Veer C, de Vos AF, van der Poll T. Myeloid-related protein-14 contributes to protective immunity in gram-negative pneumonia derived sepsis. PLoS Pathog 8: e1002987, 2012. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002987. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker BF, Lot SS, Condon TP, Cheng-Flournoy S, Lesnik EA, Sasmor HM, Bennett CF. 2′-O-(2-Methoxy)ethyl-modified anti-intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) oligonucleotides selectively increase the ICAM-1 mRNA level and inhibit formation of the ICAM-1 translation initiation complex in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 272: 11994–12000, 1997. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.18.11994. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

