Apo A-I (Apolipoprotein A-I) Vascular Gene Therapy Provides Durable Protection Against Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Rabbits
- PMID: 29122817
- PMCID: PMC5746433
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309565
Apo A-I (Apolipoprotein A-I) Vascular Gene Therapy Provides Durable Protection Against Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Rabbits
Abstract
Objective: Gene therapy that expresses apo A-I (apolipoprotein A-I) from vascular wall cells has promise for preventing and reversing atherosclerosis. Previously, we reported that transduction of carotid artery endothelial cells with a helper-dependent adenoviral (HDAd) vector expressing apo A-I reduced early (4 weeks) fatty streak development in fat-fed rabbits. Here, we tested whether the same HDAd could provide long-term protection against development of more complex lesions.
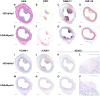
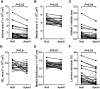
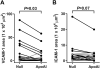
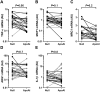
Approach and results: Fat-fed rabbits (n=25) underwent bilateral carotid artery gene transfer, with their left and right common carotids randomized to receive either a control vector (HDAdNull) or an apo A-I-expressing vector (HDAdApoAI). Twenty-four additional weeks of high-fat diet yielded complex intimal lesions containing lipid-rich macrophages as well as smooth muscle cells, often in a lesion cap. Twenty-four weeks after gene transfer, high levels of apo A-I mRNA (median ≥250-fold above background) were present in all HDAdApoAI-treated arteries. Compared with paired control HDAdNull-treated arteries in the same rabbit, HDAdApoAI-treated arteries had 30% less median intimal lesion volume (P=0.03), with concomitant reductions (23%-32%) in intimal lipid, macrophage, and smooth muscle cell content (P≤0.05 for all). HDAdApoAI-treated arteries also had decreased intimal inflammatory markers. VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1)-stained area was reduced by 36% (P=0.03), with trends toward lower expression of ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule-1), MCP-1 (monocyte chemoattractant protein 1), and TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α; 13%-39% less; P=0.06-0.1).
Conclusions: In rabbits with severe hyperlipidemia, transduction of vascular endothelial cells with an apo A-I-expressing HDAd yields at least 24 weeks of local apo A-I expression that durably reduces atherosclerotic lesion growth and intimal inflammation.
Keywords: apolipoprotein; atherosclerosis; carotid artery; gene therapy; rabbits.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures

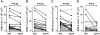
Similar articles
-
Local Vascular Gene Therapy With Apolipoprotein A-I to Promote Regression of Atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Feb;37(2):316-327. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308258. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 27932352 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of apolipoprotein A-I in rabbit carotid endothelium protects against atherosclerosis.Mol Ther. 2011 Oct;19(10):1833-41. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.133. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Mol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21772254 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibition by MCC950 Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Development in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice-Brief Report.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Aug;37(8):1457-1461. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309575. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28596375
-
Neopterin derivatives - a novel therapeutic target rather than biomarker for atherosclerosis and related diseases.Vasa. 2021 Apr;50(3):165-173. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000903. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Vasa. 2021. PMID: 32924886 Review.
-
Lipid lowering improves endothelial functions.Int J Cardiol. 2000 Jun 30;74 Suppl 1:S3-S10. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5273(99)00105-9. Int J Cardiol. 2000. PMID: 10856767 Review.
Cited by
-
HDL therapy today: from atherosclerosis, to stent compatibility to heart failure.Ann Med. 2019 Nov-Dec;51(7-8):345-359. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2019.1694695. Ann Med. 2019. PMID: 31729238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Capacity Adenoviral Vectors: Expanding the Scope of Gene Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 21;21(10):3643. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103643. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32455640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Annual Report on Sex in Preclinical Studies: Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology Publications in 2018.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Jan;40(1):e1-e9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313556. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31869272 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Serum Proteomic Analysis of Cannabis Use Disorder in Male Patients.Molecules. 2021 Sep 1;26(17):5311. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175311. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500744 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol Efflux Decreases TLR4-Target Gene Expression in Cultured Macrophages Exposed to T. brucei Ghosts.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 22;12(8):1730. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081730. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McAloon CJ, Boylan LM, Hamborg T, Stallard N, Osman F, Lim PB, Hayat SA. The changing face of cardiovascular disease 2000-2012: An analysis of the world health organisation global health estimates data. Int J Cardiol. 2016;224:256–264. - PubMed
-
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists C. Baigent C, Blackwell L, Emberson J, Holland LE, Reith C, Bhala N, Peto R, Barnes EH, Keech A, Simes J, Collins R. Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of ldl cholesterol: A meta-analysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet. 2010;376:1670–1681. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

