MicroRNA regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cell homeostasis and function in allergic inflammation
- PMID: 29122948
- PMCID: PMC5716040
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20170545
MicroRNA regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cell homeostasis and function in allergic inflammation
Abstract
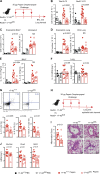
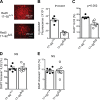
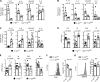
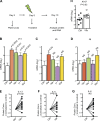
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) exert powerful effects on immunity through coordinate regulation of multiple target genes in a wide variety of cells. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) are tissue sentinel mediators of allergic inflammation. We established the physiological requirements for miRNAs in ILC2 homeostasis and immune function and compared the global miRNA repertoire of resting and activated ILC2s and T helper type 2 (TH2) cells. After exposure to the natural allergen papain, mice selectively lacking the miR-17∼92 cluster in ILC2s displayed reduced lung inflammation. Moreover, miR-17∼92-deficient ILC2s exhibited defective growth and cytokine expression in response to IL-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in vitro. The miR-17∼92 cluster member miR-19a promoted IL-13 and IL-5 production and inhibited expression of several targets, including SOCS1 and A20, signaling inhibitors that limit IL-13 and IL-5 production. These findings establish miRNAs as important regulators of ILC2 biology, reveal overlapping but nonidentical miRNA-regulated gene expression networks in ILC2s and TH2 cells, and reinforce the therapeutic potential of targeting miR-19 to alleviate pathogenic allergic responses.
© 2017 Singh et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-155 is a critical regulator of type 2 innate lymphoid cells and IL-33 signaling in experimental models of allergic airway inflammation.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Mar;139(3):1007-1016.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.06.035. Epub 2016 Aug 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27492144
-
Activation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells exacerbates and confers corticosteroid resistance to mouse nasal type 2 inflammation.Int Immunol. 2017 May 1;29(5):221-233. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxx030. Int Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28541554
-
Protein kinase Cθ controls type 2 innate lymphoid cell and TH2 responses to house dust mite allergen.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 May;139(5):1650-1666. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.044. Epub 2016 Oct 14. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27746240
-
Role of type 2 innate lymphoid cell and its related cytokines in tumor immunity.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Apr;235(4):3249-3257. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29287. Epub 2019 Oct 17. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31625163 Review.
-
Lung ILC2s link innate and adaptive responses in allergic inflammation.Trends Immunol. 2015 Mar;36(3):189-95. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Trends Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25704560 Review.
Cited by
-
Current research into A20 mediation of allergic respiratory diseases and its potential usefulness as a therapeutic target.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 28;14:1166928. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1166928. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37056760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-31 attenuates murine allergic rhinitis by suppressing interleukin-13-induced nasal epithelial inflammatory responses.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jan;23(1):42. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11680. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33179116 Free PMC article.
-
The Serum/Glucocorticoid-Regulated Kinase 1 Is Targeted by miR-19a in CD4+ T Cells.Cells. 2022 Dec 29;12(1):133. doi: 10.3390/cells12010133. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611927 Free PMC article.
-
Spotlight on microRNAs in allergy and asthma.Allergy. 2021 Jun;76(6):1661-1678. doi: 10.1111/all.14646. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Allergy. 2021. PMID: 33128813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-19 Family Impairs Adipogenesis by the Downregulation of the PPARγ Transcriptional Network.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15792. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415792. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumjohann D., Kageyama R., Clingan J.M., Morar M.M., Patel S., de Kouchkovsky D., Bannard O., Bluestone J.A., Matloubian M., Ansel K.M., and Jeker L.T.. 2013. The microRNA cluster miR-17∼92 promotes TFH cell differentiation and represses subset-inappropriate gene expression. Nat. Immunol. 14:840–848. 10.1038/ni.2642 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bronevetsky Y., Villarino A.V., Eisley C.J., Barbeau R., Barczak A.J., Heinz G.A., Kremmer E., Heissmeyer V., McManus M.T., Erle D.J., et al. . 2013. T cell activation induces proteasomal degradation of Argonaute and rapid remodeling of the microRNA repertoire. J. Exp. Med. 210:417–432. 10.1084/jem.20111717 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

