The structural basis of ryanodine receptor ion channel function
- PMID: 29122978
- PMCID: PMC5715910
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201711878
The structural basis of ryanodine receptor ion channel function
Abstract
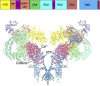
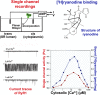
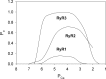
Large-conductance Ca2+ release channels known as ryanodine receptors (RyRs) mediate the release of Ca2+ from an intracellular membrane compartment, the endo/sarcoplasmic reticulum. There are three mammalian RyR isoforms: RyR1 is present in skeletal muscle; RyR2 is in heart muscle; and RyR3 is expressed at low levels in many tissues including brain, smooth muscle, and slow-twitch skeletal muscle. RyRs form large protein complexes comprising four 560-kD RyR subunits, four ∼12-kD FK506-binding proteins, and various accessory proteins including calmodulin, protein kinases, and protein phosphatases. RyRs share ∼70% sequence identity, with the greatest sequence similarity in the C-terminal region that forms the transmembrane, ion-conducting domain comprising ∼500 amino acids. The remaining ∼4,500 amino acids form the large regulatory cytoplasmic "foot" structure. Experimental evidence for Ca2+, ATP, phosphorylation, and redox-sensitive sites in the cytoplasmic structure have been described. Exogenous effectors include the two Ca2+ releasing agents caffeine and ryanodine. Recent work describing the near atomic structures of mammalian skeletal and cardiac muscle RyRs provides a structural basis for the regulation of the RyRs by their multiple effectors.
© 2017 Meissner.
Figures


References
-
- Airey J.A., Beck C.F., Murakami K., Tanksley S.J., Deerinck T.J., Ellisman M.H., and Sutko J.L.. 1990. Identification and localization of two triad junctional foot protein isoforms in mature avian fast twitch skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 265:14187–14194. - PubMed
-
- Alvarado F.J., Chen X., and Valdivia H.H.. 2017. Ablation of the cardiac ryanodine receptor phospho-site Ser2808 does not alter the adrenergic response or the progression to heart failure in mice. Elimination of the genetic background as critical variable. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 103:40–47. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.01.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson K., Lai F.A., Liu Q.Y., Rousseau E., Erickson H.P., and Meissner G.. 1989. Structural and functional characterization of the purified cardiac ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex. J. Biol. Chem. 264:1329–1335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

